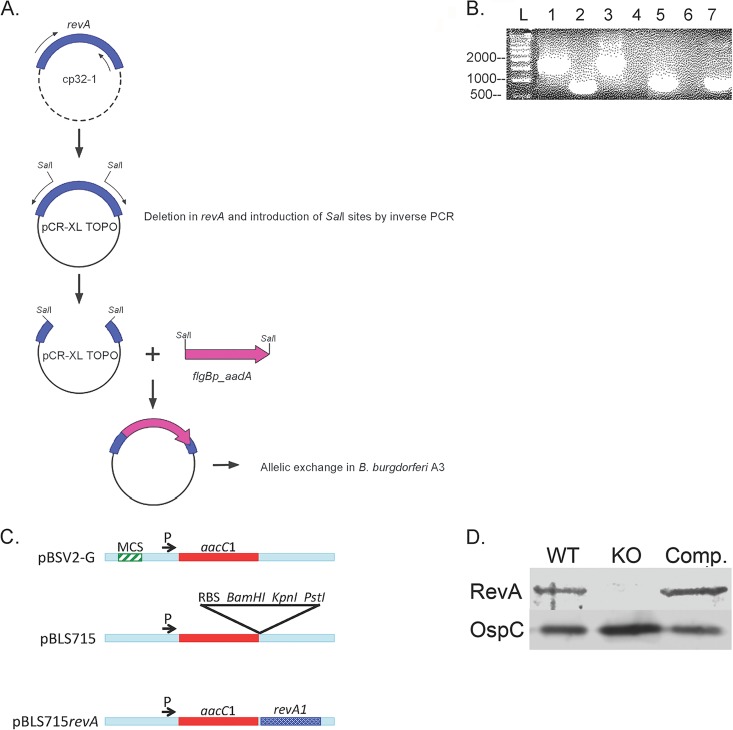
FIG 1.
Construction of the revA-deficient mutant. (A) Schematic of mutant construction. See Materials and Methods for details of cloning. (B) PCR confirmation of revA deletions by use of flanking primers for the revA6 locus (lanes 1 to 4) and primers for aad (lanes 5 to 7). Lanes 1 and 5, B31-A3ΔrevA1ΔrevA6; lanes 2 and 6, the parental strain, B31-A3; lane 3, cloning plasmid control (with the whole flanking region plus revA and the kan cassette); lane 4, no template; lane 7, cloning plasmid control (with the whole flanking region plus revA and the aad cassette). L, ladder. (C) Schematic of construction of the revA complement vector. MCS, multiple cloning site; RBS, ribosome-binding site. (D) Immunoblotting for RevA protein in whole-cell lysates. Lane 1, B31-A3 (wild type [WT]); lane 2, overloaded B31-A3ΔrevA1ΔrevA6 (knockout [KO]); lane 3, complemented strain. OspC serves as a loading control.