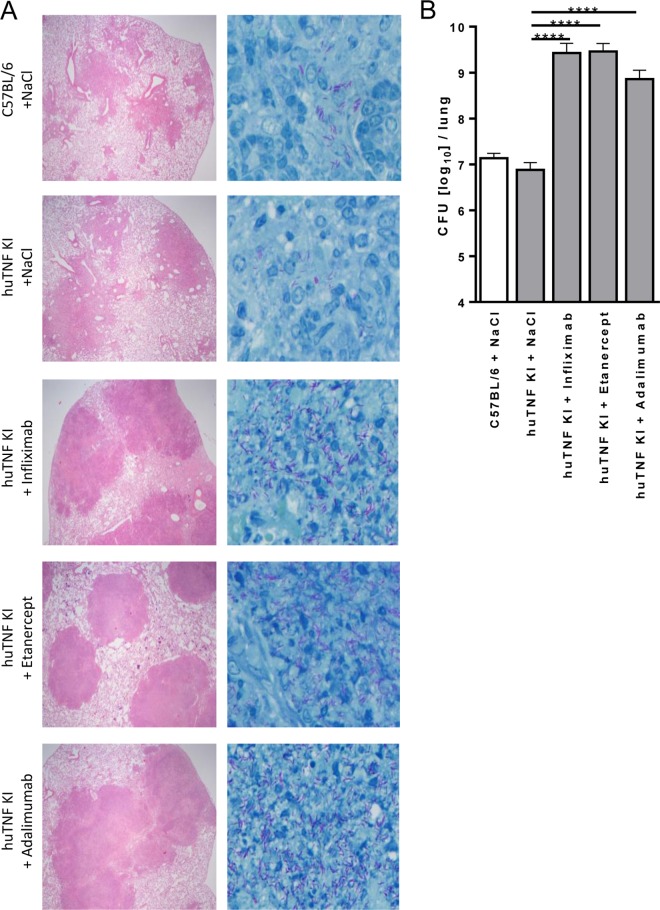
FIG 7.
Validation of the use of huTNF KI mice for evaluation and comparison of the activities of anti-human TNF compounds in M. tuberculosis-infected mice. (A) Lung pathology in WT, huTNF KI, and TNF-depleted huTNF KI mice treated with infliximab (10 mg/kg once a week), etanercept (40 mg/kg twice a week), and adalimumab (10 mg/kg once a week) after aerosol infection with M. tuberculosis. Sections obtained from diluent (NaCl)-treated and anti-TNF-treated mice at 4 weeks postinfection were stained with H&E (left) to compare the quantity and quality of granuloma formation or by the Ziehl-Neelsen method for acid-fast bacilli (right). Magnifications, ×40 (left) and ×400 (right). (B) Bacterial burden in the lungs of WT, huTNF KI, and huTNF KI mice treated with three anti-huTNF reagents at 4 weeks after aerosol infection with M. tuberculosis (n = 4 to 6 per group). Bar graphs show means ± SDs. Log-transformed data were statistically analyzed using one-way ANOVA and Bonferroni‘s post hoc test. ****, P < 0.0001 versus the vehicle-treated huTNFKI group.