Figure 2. SKIP−/− mice are more resistant to salmonellosis than congenic C57BL/6 mice.
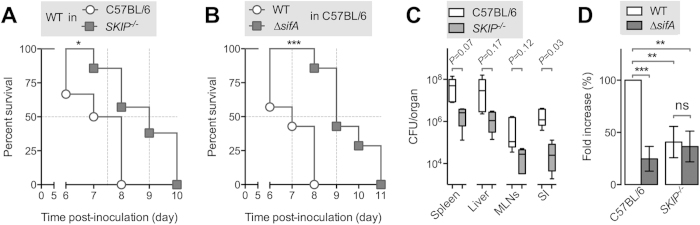
(A–C) Mice were inoculated P.O. with 105 CFU of S. Typhimurium. (A) Survival of C57BL/6 or SKIP−/− mice challenged with a wild type strain. (B) Survival of C57BL/6 challenged with a wild type or ∆sifA strain. (C) Bacterial loads in spleen, liver, mesenteric lymph nodes (MNLs) and small intestine (SI) of C57BL/6 (light box) and SKIP−/− (dark box) mice 5 days post-inoculation (5 mice per group). The data are shown as a box and whisker plot. Boxes range from the 25th to the 75th percentile and are intersected by the median line. The whiskers embrace the lowest and highest values. Unpaired t tests were used to compare group means. Two-tailed P values are indicated. (D) Bone marrow macrophages prepared from C57BL/6 or SKIP−/− mice were infected with a wild type or ∆sifA mutant strain and lysed at 2 or 16 h post-infection for enumeration of intracellular bacteria. The values shown represent the fold increase calculated as a ratio of the intracellular bacteria between 16 and 2 h and normalized to that of the wild type strain in C57BL/6-derived macrophages. Values are means ± SD of three independent experiments. Survival curves were compared using the logrank test and two-tailed P values are reported. Unpaired t-tests were used to compare two values. P values: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.
