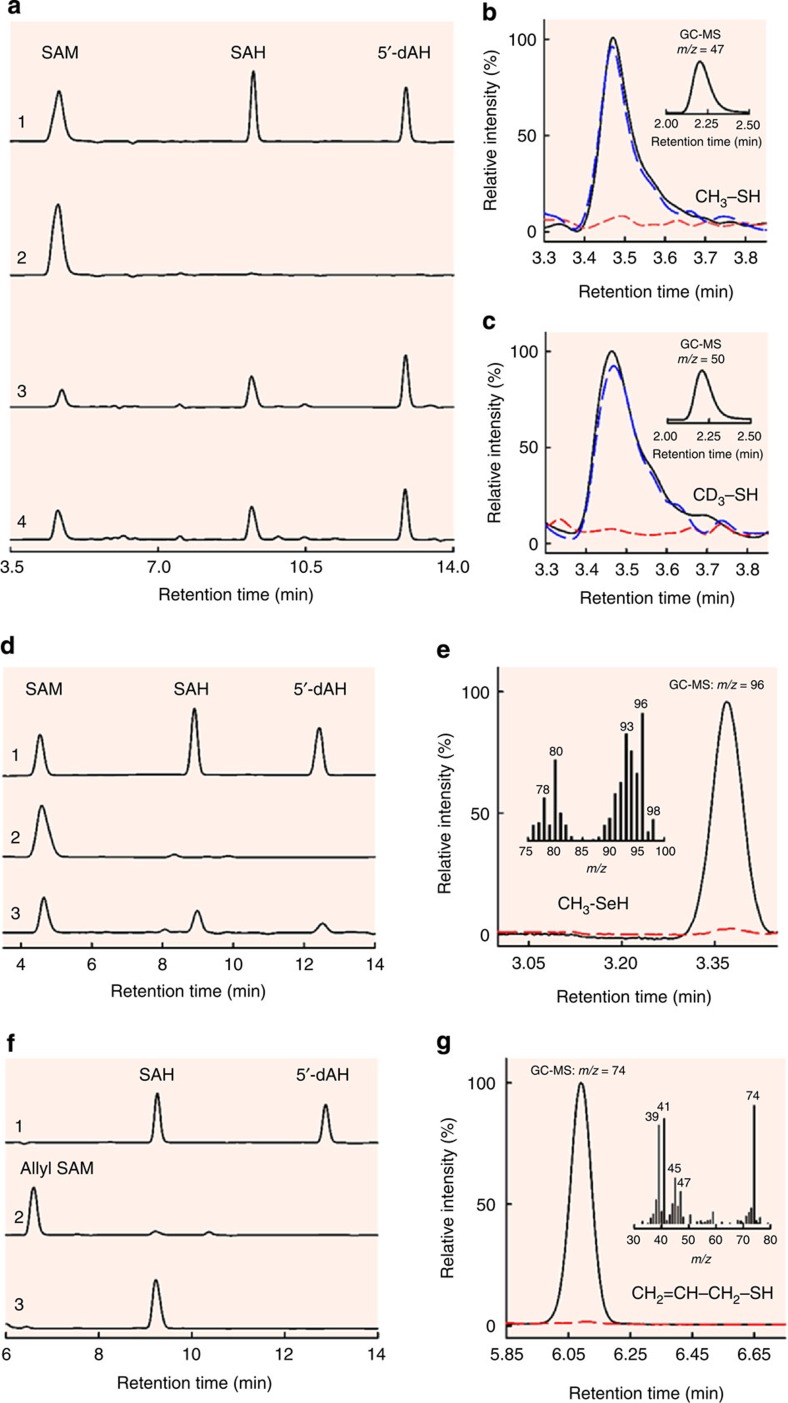
Figure 2. HPLC analyses of cleavage products of SAM/analogs and GC/GC–MS analyses of acid-quenched products upon incubation of NifEN-B/NifEN-BFeSe with SAM/analogues.
(a) HPLC elution profiles of (1) SAM, SAH and 5′-dAH standards; (2) SAM alone; (3) SAM and (4) [methyl-d3] SAM in the presence of reduced NifEN-B. (b,c) GC–MS (inset) and GC analyses of acid-quenched incubation mixtures containing SAM (b) or [methyl-d3] SAM (c), and NifEN-B in the reduced (black), oxidized (red) or re-reduced (blue) state. The acid-quenched products were identified as methanethiol (b, inset) and methane-d3-thiol (c, inset) based on their GC retention times and respective m/z ratios of 47 and 50. (d) HPLC elution profiles of (1) SAM, SAH and 5′-dAH standards; (2) SAM alone; and (3) SAM in the presence of reduced NifEN-BFeSe. (e) GC–MS full scan (inset) and SIM (m/z=96) analyses of acid-quenched incubation mixtures containing reduced NifEN-BFeSe in the presence (black) and absence (red) of SAM. The acid-quenched product was identified as methylselenol based on its GC–MS retention time and fragmentation pattern. (f) HPLC elution profiles of (1) SAH and 5′-dAH standards; (2) allyl SAM alone; and (3) allyl SAM in the presence of reduced NifEN-B. (g) GC–MS full scan (inset) and SIM (m/z=74) analyses of acid-quenched incubation mixtures containing reduced NifEN-B in the presence (black) and absence (red) of allyl SAM. The acid-quenched product was identified as allylthiol based on its GC–MS retention time and fragmentation pattern.