Fig. 1.
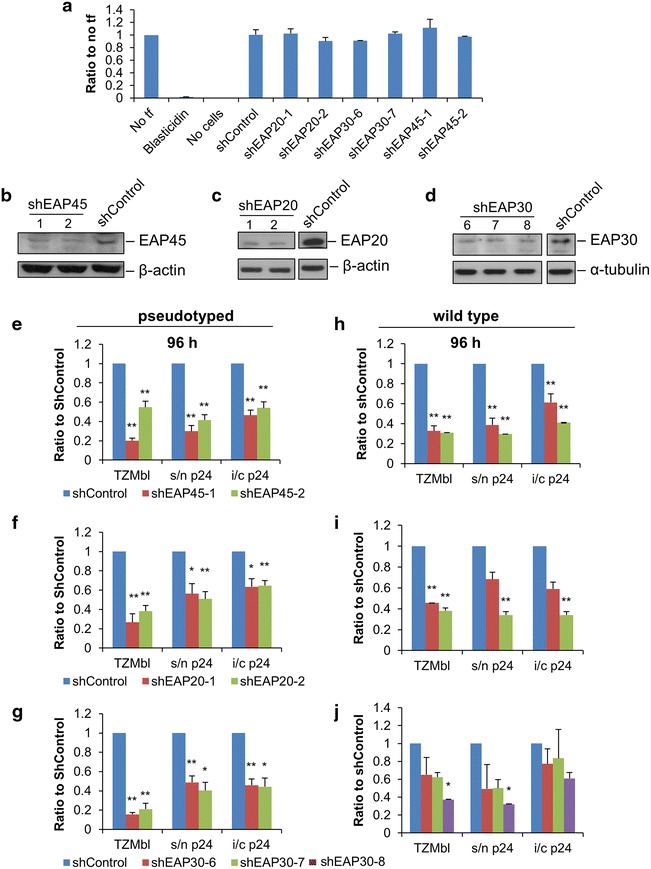
Inhibition of infectious virus production by knockdown of ESCRT-II. a Cell viability upon knockdown of ESCRT-II subunits was determined using CellTiter-Glo Luminescent Cell Viability Assay (Promega, n = 2) and normalised to that of the non-transfected control (no-tf). Cells treated with blasticidin served as a control for the viability assay. b–d Knockdown of ESCRT-II subunits in HeLaM cells. Cells were transfected with 50 ng shRNA expression plasmids using Fugene HD (Roche). Cells were harvested 96 h post-transfection and the levels of EAP20, EAP30 and EAP45 were analysed by Western blots. Detection of β-actin and α-tubulin showed equal loading. e–j Production of infectious pseudotyped (e–g) and wild type viruses (h–j) upon knockdown of ESCRT-II subunits: EAP45 (e, h), EAP20 (f, i) and EAP30 (g, j). The levels of supernatant (s/n p24) and intracellular (i/c p24) CA-p24 were quantified using ELISA. Virus infectivity was determined by infecting TZMbl cells with equal volumes of supernatant from the virus-producing HeLaM cells. Pseudotyped virus (e–g) was harvested at 96 h post-transfection (n ≥ 3). Wild type virus (h–j) was harvested at 96 h post-transfection (n ≥ 2). All bars represent the standard error of the mean (SEM); n = number of independent experiments. Unpaired, two-tailed Student’s t test with unequal variance was performed. In all figures *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.
