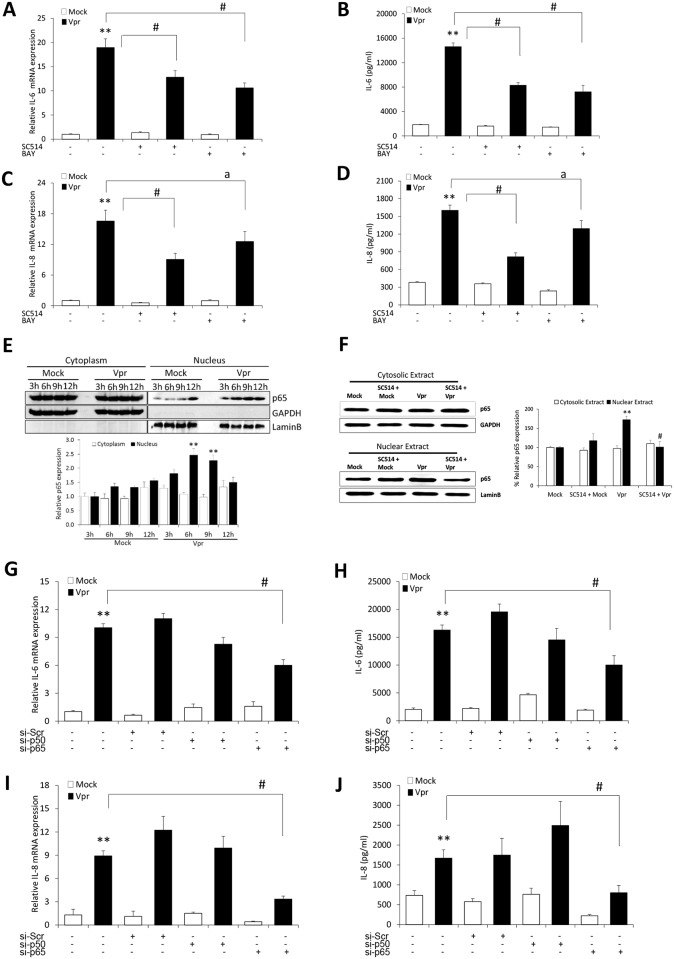
Fig 3. HIV-1 Vpr utilizes NF-κB pathway to induce IL-6 and IL-8 in SVGA astrocytes.
SVGA astrocytes were allowed to adhere overnight in 6 well plates. The cells were then 1h pre-treated with chemical inhibitor of NF-κB pathway (SC514 or BAY 1170–82) and then transfected with a plasmid encoding HIV-1 Vpr or were mock-transfected. The cells were harvested at 6h post-transfection followed by the determination of IL-6 and IL-8 mRNA expression levels using real-time RT-PCR. The cell culture supernatants were also collected at 48h post-transfection, and protein concentration of IL-6 and IL-8 was determined using BioPlex multi-cytokine assay. (A, C) mRNA expression levels of IL-6 and IL-8 calculated relative to mock-transfected controls in the presence of chemical inhibitors, respectively. (B, D) protein concentrations for secreted IL-6 and IL-8 in the presence of chemical inhibitor, respectively. (E) Time kinetics for NF-κB p-65 nuclear translocation in response to HIV-1 Vpr (F) depicts the effect of SC514 on NF-κB p-65 nuclear translocation. (G, I) portray mRNA levels while (H, J) show protein concentration for IL-6 and IL-8 when NF-κB p50 and p65 subunits were silenced. Every bar represents the mean ± SE of thee independent experiments done in triplicates. Statistical analyses were performed using 1-way ANOVA using post-hoc Tukey HSD test, # p < 0.01, a p < 0.05 as compared to Vpr transfected cells; ** p < 0.01 and * p < 0.05 compared to mock-transfected controls.