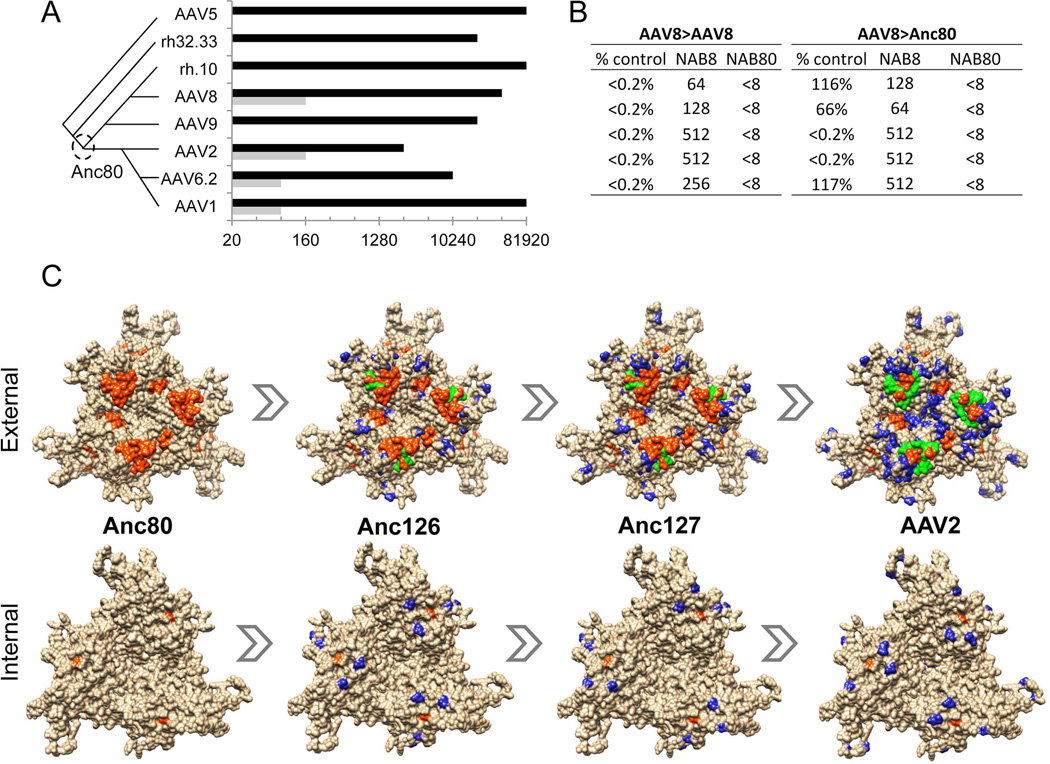
Figure 5. Immunological characterization of Anc80L65.
A. Rabbit anti-AAV serum cross-reactivity: Rabbit antiserum raised against AAV serotypes (Y-axis) was tested for NAB to Anc80L65 (grey bars) versus the homologous AAV serotype (black bars) in order to assess relative sero-cross-reactivity. Values (X-axis) represent highest dilution at which >50% neutralization is achieved. Phylogenetic relationship between immunizing serotypes is depicted schematically on the left. B. Mouse in vivo gene transfer cross-neutralization: C57Bl/6 mice received an IV injection of AAV8 or Anc80L65.CASI.EGFP.2A.A1AT 25 days following an IM injection with either saline or AAV8.TBG.nLacZ. 14 days following the second injections serum was titrated by ELISA for hA1AT expression. Table presents the relative hA1AT levels of the pre-immunized mice versus the non-immunized for each vector (% control), and the NAB titer dilutions for AAV8 (NAB8) and Anc80L65 (NAB80) 24 h prior to the second injection in the immunized group (n=5). C. A non-structural multiple sequence alignment between Anc80, Anc126, Anc127 and AAV2 VP3 sequences was generated using the Tcoffee alignment package. AAV2 trimer structure was generated using UCSF Chimera. The blue residues represent residues different from Anc80. The orange residues are defined T and B-cell epitopes on AAV2 (Gurda et al., 2013; Mingozzi et al., 2007). Green residues show the overlap between orange and blue residues to highlight mapped epitopes altered in the putative evolutionary intermediates. Human T-cell epitopes with MHC haplotype: VPQYGYLTL (B*0702), SADNNNSEY (A*0101), YHLNGRDSL (B*1501), and TTSTRTWAL (B*0801). (Mingozzi et al., 2007) Mouse B-cell epitopes of defined AAV2 antibody SADNNNS plus RGNRQ for C37B Fab (Gurda et al., 2013). In bold are the residues within each epitope that are distinct between Anc80L65 and AAV80.