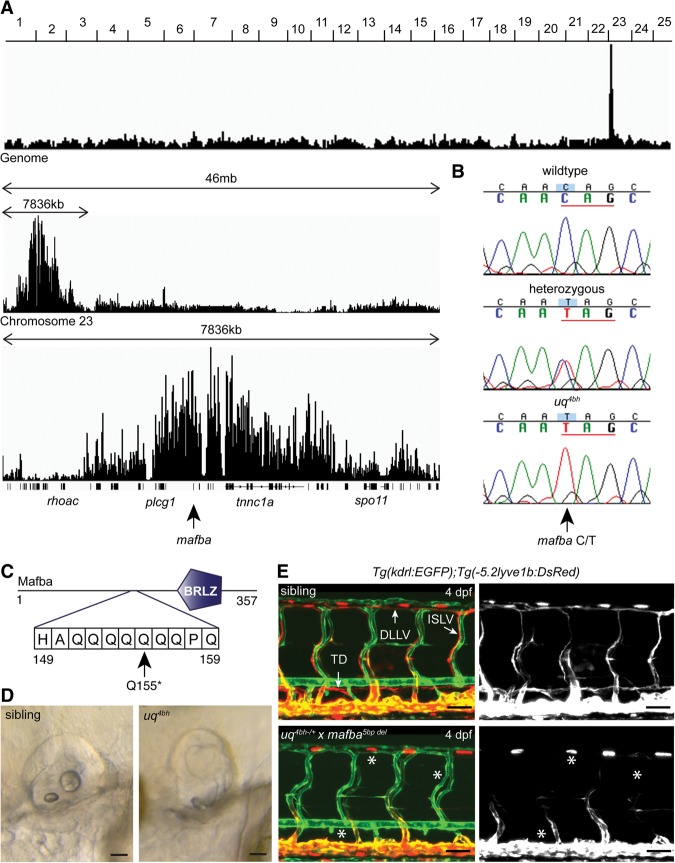
Figure 2.
Positional cloning of mafbauq4bh using whole-genome sequence-based homozygosity mapping and mutation detection. (A) Schematic plot of genomic homozygosity across all 25 chromosomes (top), chromosome 23 (middle), and the region of linkage (bottom) (see the Materials and Methods for details). The mafba gene is located centrally within the region of highest homozygosity. (B) Sequence chromatograms confirming the nonsense allele in the mafba gene. (Top) Wild type (n = 6 reads). (Middle) Heterozygous (n = 18 reads). (Bottom) Mutant (n = 19 reads). (C) Schematic of the location of the Q155* allele predicted to truncate the critical BRLZ domain of Mafba. (D) Otic vesicle morphology of sibling (left) and mutant (right) embryos at 3 dpf. Bars, 80 μm. (E) Confirmation of causative mafbauq4bh allele by complementation test with a mafba5 bp del transmitting founder. Vasculature visualized by Tg(kdrl:EGFP) (green) and Tg(-5.2lyve1b:DsRed) (red) in the sibling (top) and transheterozygous mafbauq4bh;mafba5 bp del (bottom). Siblings, n = 10; mafbauq4bh; mafba5 bp del, n = 10. (Right) Red channel. Bars, 30 μm. See also Supplemental Figure 2.