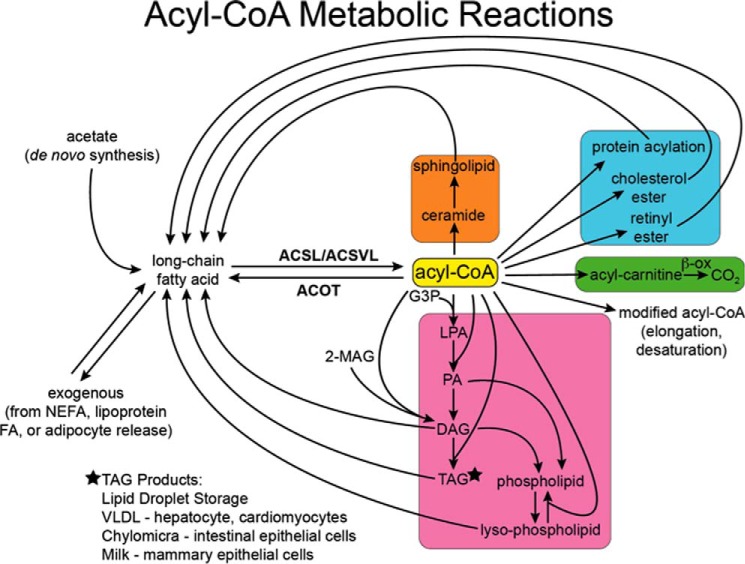
FIGURE 1.
Metabolic reactions of acyl-CoAs. Long-chain FAs are synthesized de novo from acetate or enter cells from the plasma. They are converted to acyl-CoAs by ACSL and ACSVL. The reaction is reversed by acyl-CoA thioesterases (ACOT). Acyl-CoAs can be elongated and desaturated, converted to acylcarnitines, and metabolized to CO2 via mitochondrial and peroxisomal enzymes, esterified to glycerol-3-phosphate to form lysophosphatidic acid (LPA), phosphatidic acid (PA), and TAG, and esterified to monoacylglycerol (MAG) to form diacylglycerol (DAG). Both phosphatidic acid and diacylglycerol are precursors for all the glycerophospholipids. Acyl-CoAs are also esterified to retinol and cholesterol, acylated to proteins, and incorporated into ceramide to form sphingolipids. Lipolysis of these products releases fatty acids back into cellular pools. Triacylglycerol, cholesterol esters, and retinol esters are stored in lipid droplets within cells or secreted from specialized cells as lipoproteins or milk constituents. NEFA, non-esterified fatty acid.