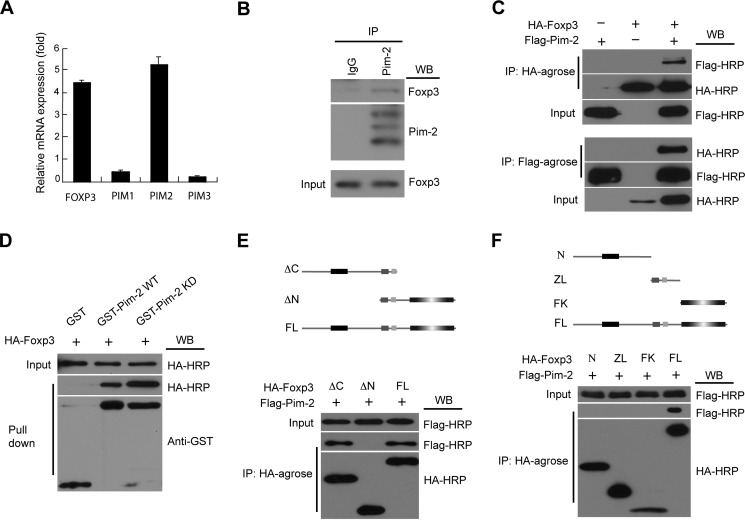
FIGURE 1.
Pim-2 is highly expressed in Treg cells and physically associates with Foxp3. A, human CD4+CD25+ Treg cells were sorted from human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. The expression profile of PIM kinases in Treg cells was assessed by real-time qRT-PCR analysis. B, representative immunoblotting data showing the endogenous association between Pim-2 and Foxp3 in mouse splenocytes. Cell lysates of splenocytes were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with antibody to Pim-2 or control IgG and then subjected to Western blot (WB) analysis with antibodies to Foxp3 and Pim-2. Bottom panel, Foxp3 protein in whole lysates. C, the in vitro association between Pim-2 and Foxp3 was analyzed in HEK293T cells by coimmunoprecipitation assay. The lysates from 293T cells, cotransfected with HA-Foxp3 and FLAG-Pim-2 expression plasmids, were immunoprecipitated with HA-agarose (top panel) and FLAG-agarose (bottom panel) and then analyzed by Western blotting with anti-FLAG-HRP and anti-HA-HRP as indicated. D, Foxp3 could be pulled down by the GST-Pim-2 WT/KD fusion protein in vitro. E and F, both the N-terminal domain and the zinc finger and leucine zipper domain of Foxp3 were required for the association between Foxp3 and Pim-2. Top panel, schematic of the Foxp3 fragments. N, N-terminal domain; ZL, zinc finger and leucine zipper domain; FK, forkhead domain; ΔC, forkhead truncated fragment; ΔN, N-terminal domain truncated fragment; FL, full-length Foxp3.