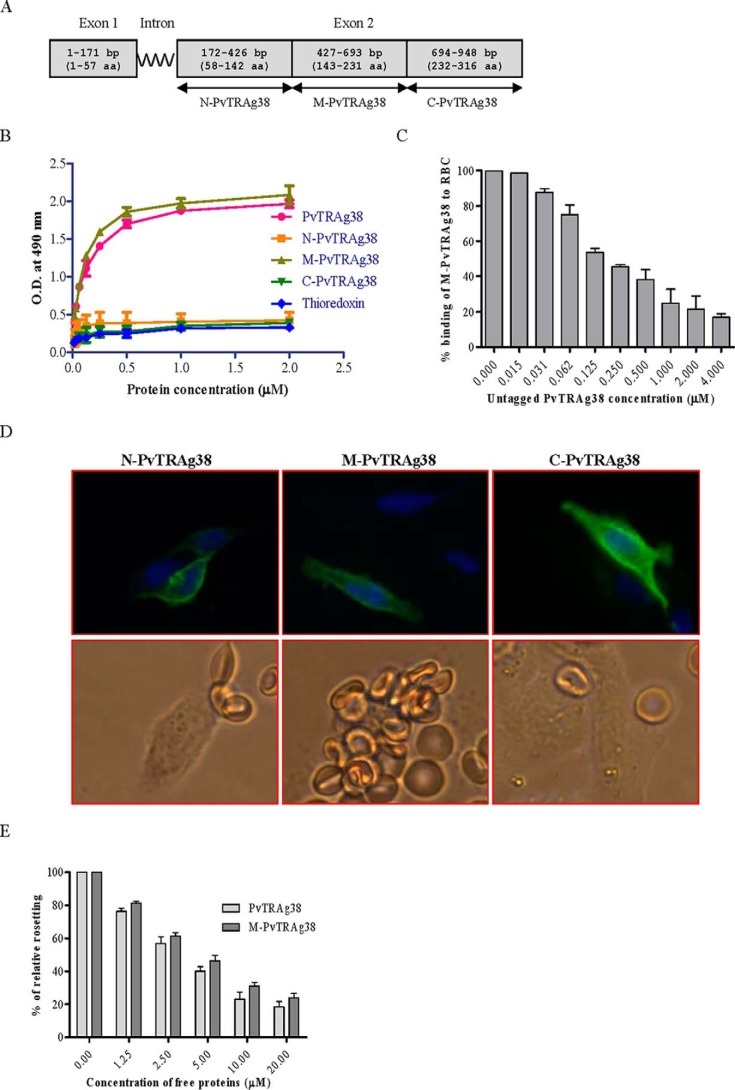
FIGURE 2.
Binding of PvTRAg38 fragments to human erythrocytes. A, PvTRAg38 encoded by exon 2 was divided in to three (N-terminal, middle, and C-terminal) parts. These DNA fragments were PCR-amplified, cloned, and expressed in E. coli for Cell-ELISA or in mammalian cell line CHO-K1 for rosetting assay. B, erythrocyte binding activity of PvTRAg38 fragments by Cell-ELISA. Each well of the ELISA plate was coated with ∼1 million erythrocytes and reacted with different concentrations (0–2 μm) of histidine-tagged recombinant PvTRAg38 and its fragments. The plate was developed with mouse anti-His6 monoclonal antibody as described in the text. C, specificity of erythrocyte binding to M-PvTRAg38 fragment by competition assay. For this, a mixture of histidine-tagged recombinant M-PvTRAg38 (200 nm) and variable amounts (0–4 μm) of untagged PvTRAg38 were added to ∼1 million RBCs coated in each well of the ELISA plate. The plate was developed with mouse anti-His6 monoclonal antibody as described in the text. Binding in the absence of untagged PvTRAg38 was taken as percentage control for rest of the concentrations. D, erythrocyte binding activity of PvTRAg38 fragments by rosetting assay. PvTRAg38 fragments were expressed on the surface of the transfected CHO-K1 cells, detected by the mouse monoclonal antibody DL6 as in Fig. 1 (green fluorescence). The nuclei were stained with DAPI (blue color). Merged images of blue and green fluorescence are shown in the upper panels. The lower panels show the rosette formation where transfected CHO-K1 cell is binding to more than five erythrocytes. E, specificity of binding of PvTRAg38 and its fragment M-PvTRAg38 expressed on CHO-K1 cells to erythrocytes by competition assay. Erythrocytes (1% hematocrit) were preincubated with different concentrations of histidine-tagged PvTRAg38 or M-PvTRAg38 (0–20 μm) for 1 h at 37 °C. They were then allowed to bind to RE4-PvTRAg38 transfected CHO-K1 cells at 37 °C for 1 h. The results were expressed as relative binding to positive control (binding of PvTRAg38 transfected cells with untreated RBCs). The mean and ± standard deviation of three experiments is reported.