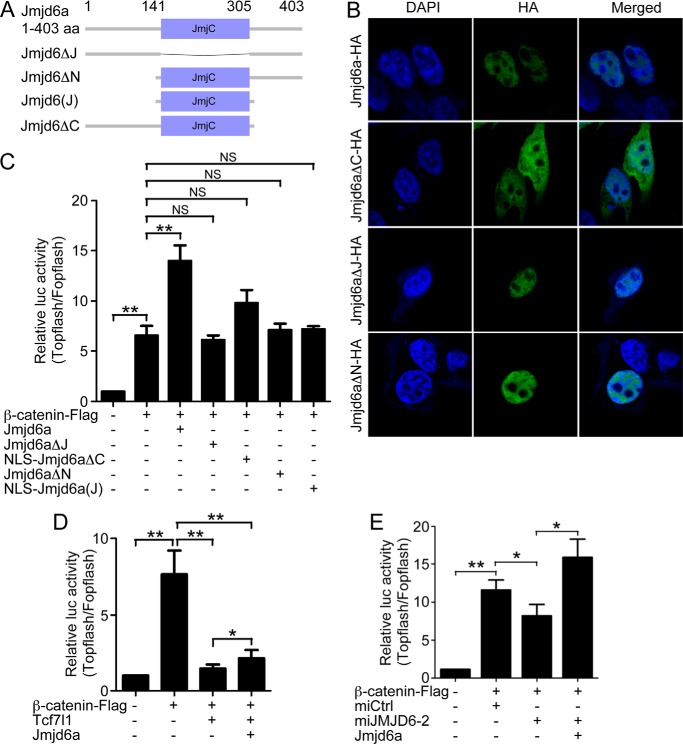
FIGURE 4.
Jmjd6 enhances Wnt signaling. A, domain structure and construction of the deletion mutants of X. laevis Jmjd6a used in this study. B, subcellular localizations of the Jmjd6 mutants revealed by immunofluorescence. Jmjd6 without the C-terminal region lost nuclear localization and distributed ubiquitously throughout the whole cell. C, Jmjd6 strongly enhanced β-catenin-stimulated reporter activity, whereas the deletion mutants of Jmjd6 did not show such an enhancing effect. Error bars represent mean ± S.E. of four replicates. **, p < 0.01; NS, not significant. D, Tcf7l1 overexpression showed a strong repressive effect on β-catenin-stimulated reporter activity, whereas cotransfection of the plasmid for Jmjd6 led to a significant alleviation of the repressive effect. Error bars represent mean ± S.E. of four replicates. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01. E, Jmjd6 is required for β-catenin-stimulated transcription. In HEK293T cells, β-catenin strongly stimulated the reporter activity. Simultaneous knockdown of endogenous JMJD6 compromised the stimulation of the reporter activity, which was then rescued by the cotransfection of the plasmid for X. laevis Jmjd6a. Error bars represent mean ± S.E. of four replicates. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01.