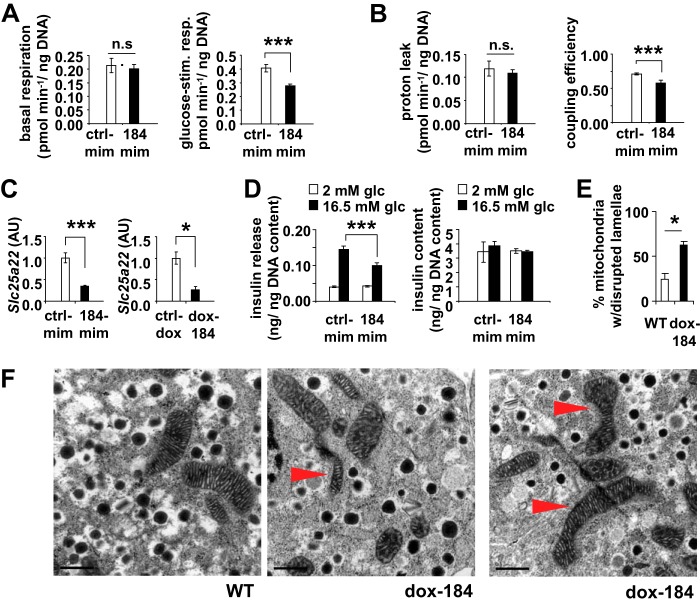
FIGURE 5.
miR-184 impacts mitochondrial respiration. Measurements of basal respiration and glucose-stimulated respiration (A), proton leak and mitochondrial coupling efficiency (n = 3) in MIN6 cells transfected with either control or 184-mimic (B), and qRT-PCR analysis of miR-184-targeted gene Slc25a22 in MIN6 cells transfected with either control or 184-mimic and in the islets of dox-184 transgenic mice (C), respectively. n.s., not significant; AU, arbitrary units. D, reduced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion in MIN6 cells transfected with either control or 184-mimic. Results are presented as the mean ± S.E. *, p < 0.05; ***, p < 0.001. E, analysis of mitochondria from the beta cells within the islets isolated from WT ctrl-dox and dox-184 mice that received 1 mg/ml doxycycline for 15 days. Data are represented as the percentage of mitochondria with disrupted lamellae. F, transmission electron microscopic (TEM) images of the beta cells within the islets from WT and dox-184 mice that received 1 mg/ml doxycycline for 15 days. Scale bar 0.5 μm.