FIGURE 1.
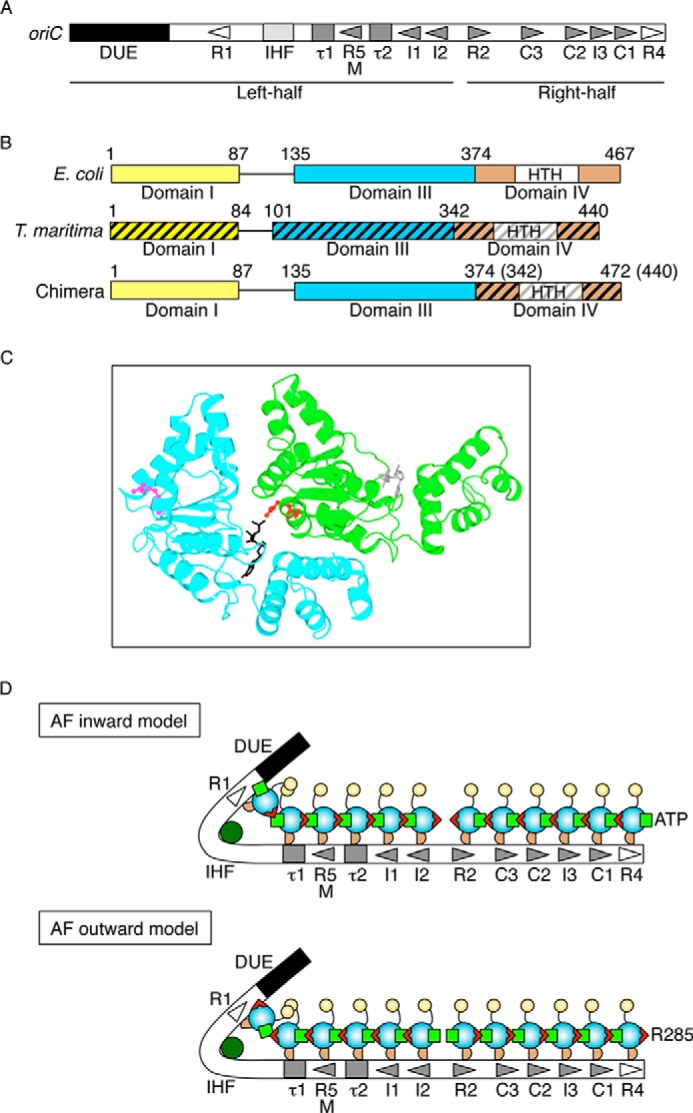
Structures of oriC and DnaA and models for DnaA complexes. A, overall structure of oriC. oriC (245 bp) includes DUE (black bar), IHF-binding site (IHF; light gray box), and multiple DnaA boxes (triangles and gray boxes). High affinity sites (R1 and R4) are indicated by an open symbol. Moderate (R2) and low affinity (R5M, τ1-2, I1-3, and C1-3) sites are indicated by filled gray symbols. The left-half and right-half regions of oriC are also indicated. B, DnaA domain structure of chiDnaA. Domains of EcoDnaA (E. coli) and TmaDnaA (T. maritima) are indicated by open and hatched boxes, respectively, corresponding to domains I, III, and IV. Lines indicate domain II. Boxes labeled HTH indicate the helix-turn-helix motif within domain IV. Domain boundary amino acid numbers are indicated. The chimeric protein constructed in this work (chiDnaA; 472 amino acid residues) contains EcoDnaA domains I–III (amino acids 1–374) and the TmaDnaA domain IV (amino acids 342–440). C, model of a dimeric structure of DnaA domain III. A homology model constructed previously using TmaDnaA sequence is shown (19). Each protomer is colored differently. The Arg finger motif of each protomer is shown using a ball-and-stick model and colored in red or pink. The bound ADP is shown using a stick model and colored in black or gray. D, models for DnaA assembly structure on oriC. DnaA domains I, II, III, and IV are indicated by a yellow circle, a curved line, a cyan circle, and a brown half circle, respectively. Domain III carries the Arg finger motif (red triangle) and bound ATP (light green square) at opposite sides of the tertiary structure. DnaA forms a homo-oligomer with a head-to-tail configuration that depends on the interaction between the Arg finger and ATP of flanking protomers. Each DnaA binds to one DnaA box. Generally, DnaA boxes in the left half of oriC and those in the right half of oriC have opposite orientations. IHF is shown in dark green. In the Arg finger-inward model (AF-inward; top), subcomplexes of DnaA formed on each oriC region have the Arg finger facing inward within oriC and the bound ATP facing outward from oriC. Conversely, in the Arg finger-outward model (AF-outward; bottom), subcomplexes of DnaA formed on each oriC region have the Arg finger facing outward from oriC and the bound ATP facing inward within oriC.
