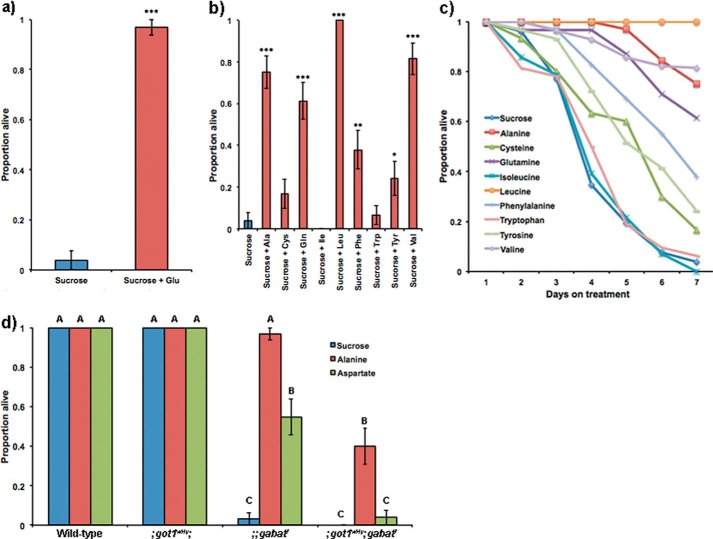
FIGURE 5.
Deficiency in glutamate causes the metabolic phenotype of gabatf. a, glutamate rescues the metabolic phenotype of gabatf. When supplementing sucrose food with glutamate (final concentration = 0.05 m), the metabolic phenotype of gabatf mutant males is rescued. Fisher's exact test, ***, p < 0.0005. b, specific amino acids rescue the metabolic phenotype of gabatf males. When we supplement the sucrose diet with the nine amino acids that can be metabolized into glutamate by specific aminotransferases, we found that the following amino acids rescue the metabolic phenotype: alanine, glutamine, leucine, phenylalanine, tyrosine, and valine. Fisher's exact test, *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.005; ***, p < 0.0005. c, survival curves of gabatf flies on specific diets. Using data from b, we plotted the proportion of live gabatf mutants as a function of the number of days the mutants were given a specific diet. Rescue data from b were compared on day 7. d, GOT1 mediates the metabolic rescue of gabatf by alanine. We placed males of our wild-type, gabatf, ;got1wHy;, and got1wHy;;gabatf strain on alanine, aspartate, and sucrose food. A one-way ANOVA between subjects was conducted to compare the effect of a food treatment on survival among wild-type, gabatf, ;got1wHy;, and ;got1wHy;gabatf strains. There was a significant effect of the food treatment on survival for the 12 groups (F(11) = 156.1, p < 0.0001). When combined with ;got1wHy;, the metabolic phenotype of gabatf cannot be rescued by alanine or aspartate. Different levels (A–C) indicate statistical significance according to Tukey post hoc tests.