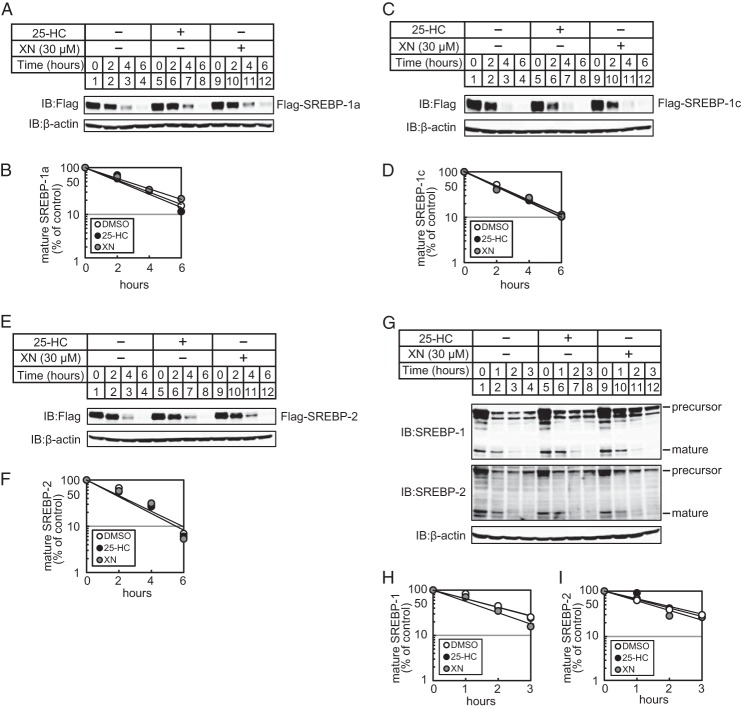
FIGURE 3.
XN does not promote the degradation of mature SREBPs. A, C, and E, CHO-7 cells were transfected with pCMV-3×FLAG-SREBP-1a (2–487) (A), pCMV-3×FLAG-SREBP-1c(2–463) (C), or pCMV-3×FLAG-SREBP-2 (2–481) (E) and cultured in medium E for 24 h. The cells were trypsinized and seeded in 6-well plates and cultured further under the same conditions for 24 h. After incubation with 50 μm cycloheximide for 0.5 h, the cells were switched to medium E supplemented with 50 μm cycloheximide in the presence of vehicle, 1 μg/ml 25-HC, or 30 μm XN. G, CHO-7 cells were depleted of sterols by incubating in medium F for 16 h. After incubation with 300 μm AEBSF for 0.5 h, the cells were switched to medium F supplemented with 300 μm AEBSF in the presence of vehicle, 1 μg/ml 25-HC, or 30 μm XN. After incubation for the indicated period of time, whole cell extracts underwent immunoblotting (IB) with anti-FLAG, anti-SREBP-1 (2A4), anti-SREBP-2, or anti-β-actin antibodies. B, D, F, H, and I, The signals detected on the membrane in (A, C, E, and G) were quantified, and data were plotted as the percentage of FLAG-SREBP-1a (B), FLAG-SREBP-1c (D), FLAG-SREBP-2 (E), mature SREBP-1 (H), and -2 (I) protein remaining. The same results were obtained in more than three separate experiments.