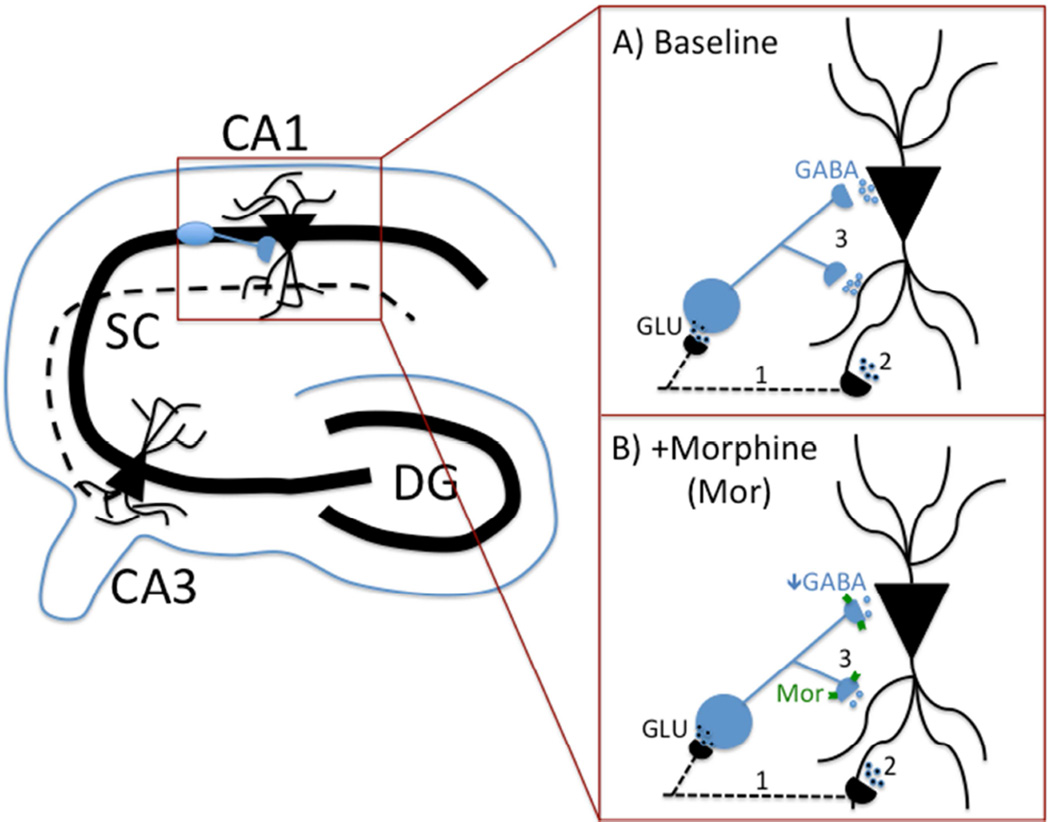
Figure 1. Schematic highlighting MOPR role in hippocampal circuit.
(A, B) Shaffer Collateral projections (represented by dotted line) from pyramidal cells in CA3 synapse with dendrites of CA1 pyramidal cells as well as local inhibitory interneurons (shown in blue). A) Thus, stimulating CA3 axons (1) will produce direct activation of CA1 dendrites (2) as well as indirect (i.e., feed-forward) inhibition of these dendrites/cell b odies through GABAergic interneuron activation (3). B) MOPR activation (e.g., with DAMGO or morphine) during CA3 axonal firing (1) will decrease GABA release from the interneuron (3), resulting in a net increase in excitatory influences on CA1 pyramidal cells (2).