Figure 2.
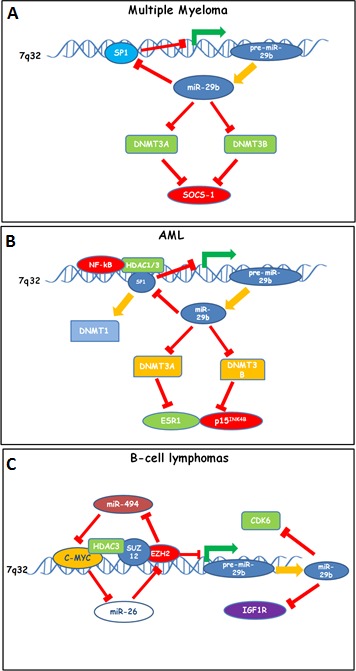
Down-modulation of miR-29b by epigenetic feedback loops sustaining proliferation and survival of (A) Multiple Myeloma, (B) AML and (C) B-cell lymphoma cells. A. In MM cells, SP1 acts by repressing miR-29b promoter thus reducing miR-29b expression; miR-29b in turn targets SP1, DNMT3A and DNMT3B, thus inducing global DNA hypomethylation and reactivation of SOCS-1 by promoter hypomethylation. B. In AML cells, a molecular complex formed by HDAC1-3/NF-kB and SP1 represses miR-29b promoter transcription. In turn, miR-29b targets SP1, a DNMT-1 transactivator, DNMT3A and DNMT3B, thus up-regulating ESR1 and p15 by promoter hypomethylation. C. In aggressive B-cell lymphomas, repression of miR-29b is accomplished by a multimeric complex comprising c-MYC, HDAC3, SUZ12 and EZH2 which represses miR-29b promoter. Of note, EZH2 causes H3K27me3-dependent repression of miR-494, thus up-regulating the miR-494 target c-MYC, which in turn promotes EZH2 expression by inhibiting miR-26. miR-29b-dependent anti-proliferative effects in B-cell lymphomas rely on CDK6 and IGF1R targeting.
