Figure 3. c-Src suppression reduces Cyr61 in MDA-MB-231-Tet-On-shRNA-c-Src and in SUM159PT cells.
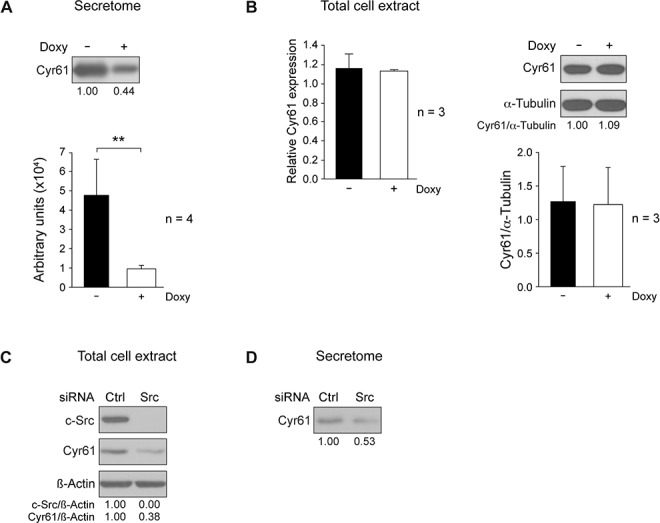
A. Conditioned media from equal number of control or Doxy-treated MDA-MB-231-Tet-On-shRNA-c-Src were used to prepare secretome (S3 fraction) by centrifugation as in Figure 4A. After concentration by methanol/chloroform precipitation, pellet was used for detection of Cyr61 by immunoblotting. Quantitation of 4 independent experiments by ImageJ is shown. B. Analysis of Cyr61 mRNA and protein in total cell extracts from control and Doxy-treated (2 μg/ml) cultures grown for 72 h. Cyr61 (CCN1) mRNA expression was determined by qRT-PCR employing GAPDH as endogenous control (see Materials and Methods). Results are shown as mean ± SD of relative Cyr61 mRNA levels in three independent experiments in triplicate, considering arbitrarily the first sample of Doxy-untreated cells triplicate as 1. Intracellular Cyr61 was analyzed by immunoblotting, and α-tubulin was used for loading control. Quantitation of 3 independent experiments by ImageJ is shown. (**p < 0.01). C. c-Src was suppressed in SUM159PT cells by transient transfection of siRNA-hs-c-Src (see Materials and Methods), and levels of c-Src and Cyr61 were determined by immunoblotting in total cell extracts. D. Detection of Cyr61 levels in the secretome derived from equal number of SUM159PT cells after c-Src depletion.
