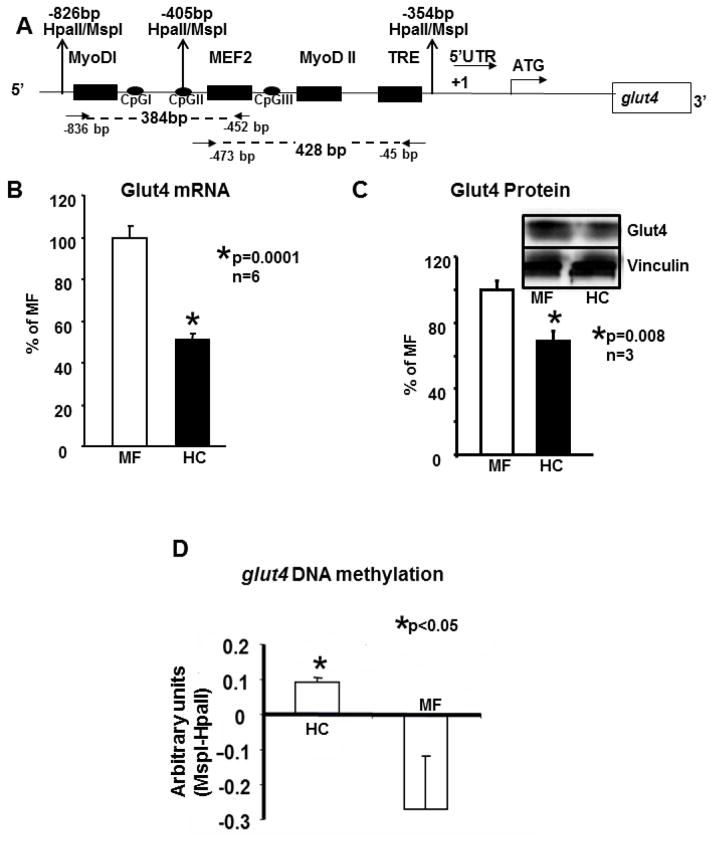
Figure 1.
A. Schematic representation of the one kb upstream region of the rat glut4 gene cloned in a pGL3 vector.
One kb of the rat glut4 promoter region is depicted. This region contains the MyoD-I, MyoD-II, MEF2 and the TRE DNA binding consensus elements 5′- to the transcriptional (+1) and translational (ATG) start sites. In addition the three CpG sites, I, II and III and the MspI/HpaII restriction enzyme sites are shown. Arrows show the location of forward and reverse primers employed to generate the 384 bp and 428 bp amplification DNA fragments (shown as dotted lines) for chromatin immunoprecipitation assays. B. Skeletal muscle Glut4 mRNA. In 100 day old skeletal muscle of early postnatal mother fed (MF) and high carbohydrate (HC) fed male rats, RT-qPCR assessment of Glut4 mRNA employing β-actin as the control gene. The relative expression of Glut4 is shown as a percent of MF value depicted as 100%. Data are shown as mean ± SEM of triplicate determinations in an n=6 samples for each group, *p<0.0001 between the two groups. C. Skeletal muscle Glut4 protein. The inset demonstrates representative Western blots showing Glut4 (above) and vinculin (internal control, below) protein bands in MF and HC groups. Quantification of 100d old skeletal muscle Glut4 protein concentrations as a ratio to vinculin is depicted as a percent of MF. Mean±SEM values are shown in an n=3 for each group, *p=0.008. D. Global methylation of rat skeletal muscle glut4 promoter around MyoDI-TRE region and difference in quantification of the glut4 bands. Southern blot analysis of MspI or HpaII digested genomic DNA obtained from the 100 day old skeletal muscle of MF and HC groups was quantified (after expression as a ratio to β-actin loading control) as a difference between corresponding MspI and HpaII digestions. Data is shown as Mean±SEM for an n=6 each, *p<0.05.