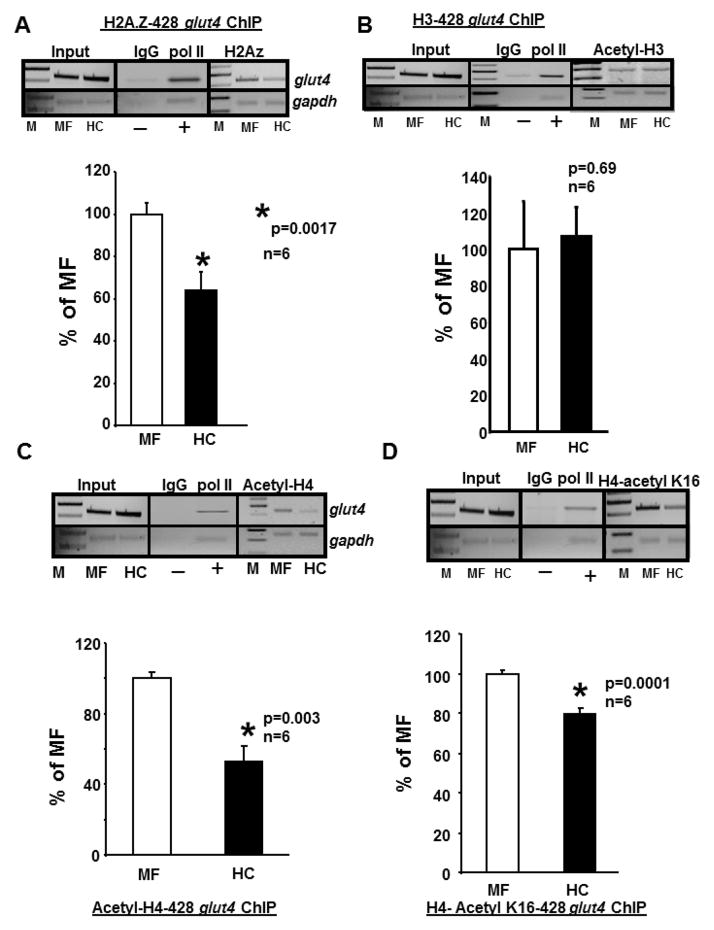
Figure 4. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays demonstrating histones (H) associated with the glut4 gene.
A–D. Top panels - Representative 2% agarose gels demonstrate the input chromatin PCR amplified glut4 (top gels) and gapdh control (bottom gels) without an antibody (left panels), in the presence of nonspecific (IgG, −) and anti-polymerase II (pol II, +) IgGs (middle panels), and ChIP assay demonstrating the PCR amplification products of the 428 bp glut4 DNA or 230 bp gapdh DNA (internal control) from 100 day old male MF and HC skeletal muscle chromatin in the presence of anti-H2A.Z (A), anti-H3 (B), anti-H4 (C) or anti-H4, lysine (K)16 (D) IgGs. Bottom panels depict the quantification of the 428 bp glut4 amplification product in the H2A.Z (A), H3 (B), H4 (C) or H4.K16 (D) ChIP as a ratio to that of gapdh DNA after correction for the input control and expressed as a percent of MF. M = DNA size markers, *p=0.0017 (A), p=0.69 (B), *p=0.003 (C), *p=0.0001 (D), n=6 samples for each histone and in each experimental group.