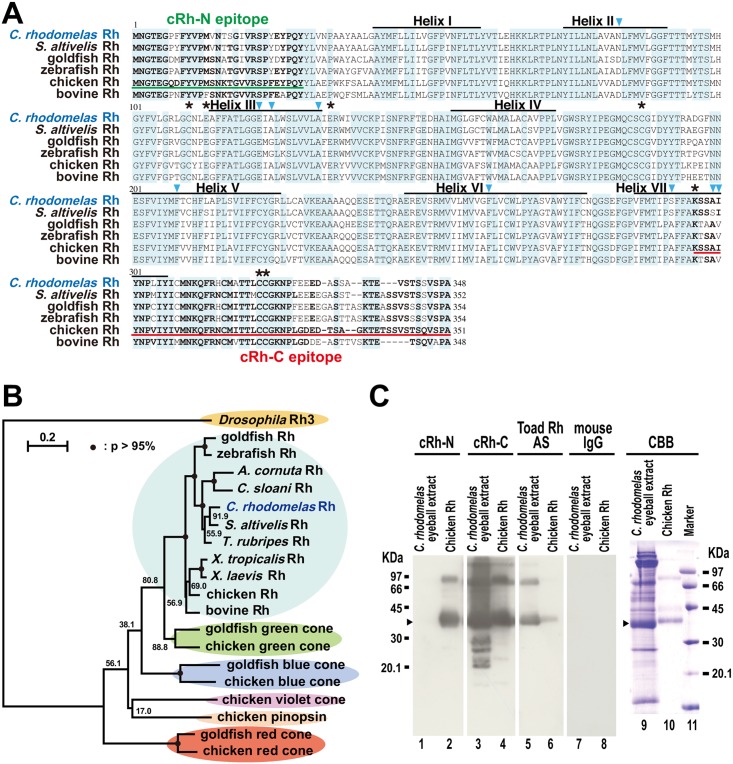
Fig 2. Sequence analysis and immunoblot detection of CrRh.
(A) Amino acid sequences of CrRh and the other opsins. Alignment of CrRh and representative members of vertebrate rhodopsins are shown. Amino acid sequences except for CrRh (present study) were obtained from the NCBI Entrez Protein database. S. altivelis is the deep-sea rockfish lonspine thornyhead [29]. Amino acids sequences were aligned using CLUSTAL W software. Blue-colored boxes indicate conserved regions in all members. Asterisks indicate amino acid positions with functionally important residues. Arrowheads indicate positions for spectral tuning sites based on previous study [16]. Black lines show transmembrane regions. cRh-N epitope is the epitope of polyclonal antibody (cRh-N) which recognizes N-terminal region of chicken rhodopsin (Met1-Tyr29, [25]). cRh-C epitope is the epitope of polyclonal antibody (cRh-C) which recognizes C-terminal region of chicken rhodopsin (Lys296-Ala351). Bold letters in the epitope regions denote amino acids identical to those of chicken rhodopsin. (B) A phylogenetic tree of opsin family proteins constructed by Neighbor-Joining method. Amino acid sequences except for A. cornuta rhodopsin [16], C. sloani rhodopsin [16], and CrRh (present study) were obtained from the NCBI Entrez Protein database. They were analyzed in the conserved region of the Rh family proteins using CLUSTAL W and NJ plot software (version 2.3). Bootstrap probabilities (p) are represented by closed circles on the nodes (p > 95%) or values near the nodes. Accession numbers for sequences obtained from the NCBI Entrez Protein database are M17718 (Drosophila Rh3), L11863 (Goldfish Rh), NM_131084 (Zebrafish Rh), DQ490124 (Sebastolobus altivelis Rh), NM_001078631 (Takifugu rubripes Rh), NM_001097334 (Xenopus tropicalis Rh), NM_001087048 (Xenopus laevis Rh), NM_001030606 (Chicken Rh), NM_001014890 (Bovine Rh), L11866 (Goldfish green cone), M92038.1 (Chicken green cone), L11864 (Goldfish blue cone), NM_205517 (Chicken blue cone), NM_205438 (Chicken violet cone), NM_205409 (Chicken pinopsin), L11867 (Goldfish red cone), and NM_205440 (Chicken red cone). (C) Western blot analysis and CBB stain of C. rhodomelas ocular proteins. For western blotting (lanes 1–8), eyeball extract corresponding to a presumed 0.01 retina (containing 0.0012 ODml of CrRh) of C. rhodomelas or purified chicken rhodopsin (chicken Rh, 0.5 μg, [27]) was loaded in each lane. For CBB stain (lanes 9–11), the larger amount of the extract (0.03 retina, 0.0036 ODml of CrRh) and purified chicken rhodopsin (3 μg) was loaded. Anti-rhodopsin antibodies used were: cRh-N, anti-N-terminal region of chicken rhodopsin (Met1-Tyr29, [25]); cRh-C, anti-C-terminal region of chicken rhodopsin (Lys296-Ala351); Toad Rh AS, anti-toad rhodopsin antiserum [24]. Concentration and dilution of the antibodies were: cRh-N (1000-fold dilution), cRh-C (2.9 ng/ml) and Toad Rh-AS (1000-fold dilution). Control anti-mouse IgG antibody was used at 2.9 ng/ml. Arrowheads indicate signals considered as monomeric form of CrRh.