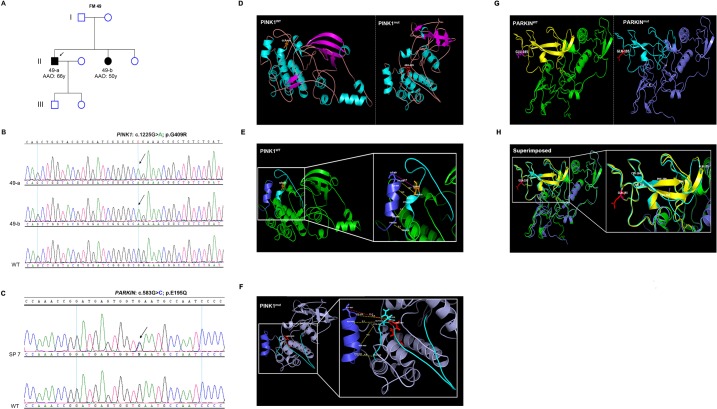
Fig 1. Genetic characterization of PARKIN (p.G409R) and PINK1 (p.E195Q) variants and their predicted functional impact.
(A) Pedigree of FM 49 with LOPD. (B) Part of the sequencing chromatogram of PINK1 exon 6 showing homozygous c.1225G>A mutation (corresponding to p.G409R substitution) in 49-a and 49-b but not in WT. (C) Part of the sequencing chromatogram of PARKIN exon 5 showing heterozygous c.583G>C variant (corresponding to p.E195Q substitution) in SP-7. (D) Ribbon presentation of PINK1WT and PINK1mut structural models. The secondary structures are colored as follows: β-strands (magenta), α-helices (cyan), coils (light pink). (E) PINK1WT. (F) PINK1mut. The spatial distance between the P+1 binding motif (cyan) and helix G (blue), measured in Angstrom (Å), is increased in PINK1mut compared to PINK1WT. A close-up view of the activation loop (aa 384–417) containing the P+1 binding motif and the helix G is represented [27, 28]. (G and H) p.E195Q has a very subtle impact on the protein conformation. Ribbon presentation of PARKINWT and PARKINmut structural models. The UPD, is shown in (yellow) or (cyan) in PARKINWT and PARKINmut, respectively. (G) Positions of the missing β-strand and α-helix are indicated by the asterisk and the hash symbols, respectively. (H) Superimposition of PARKINWT and PARKINmut showing parts of the protein (indicated by a hash symbol) that had lost the β-strand structure and adopted a random coil instead. Age at onset: AAO. Years: y. WT: wild-type.