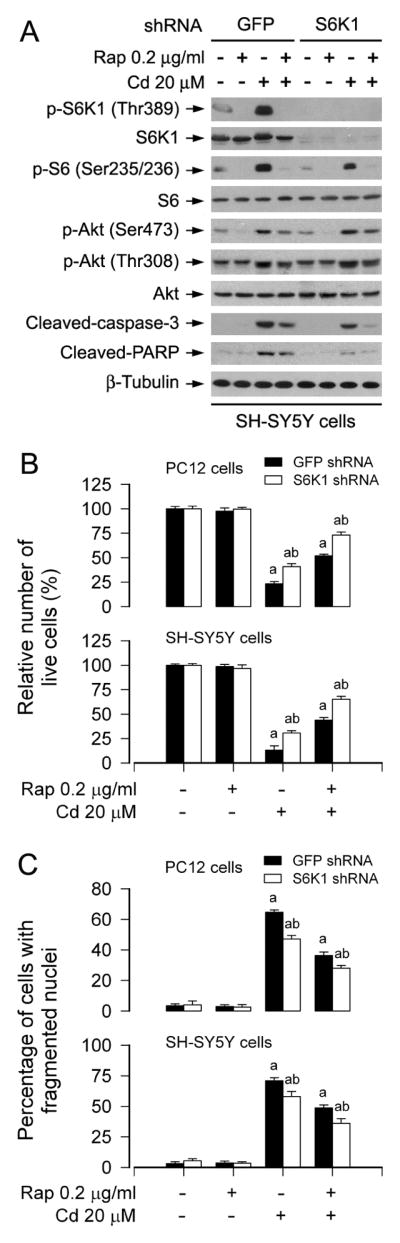
Fig. 4.
Rapamycin prevents Cd-induced neuronal cell death by targeting mTORC1-mediated S6K1 pathway. PC12 and SH-SY5Y cells, infected with lentiviral shRNA to S6K1 or GFP (as control), were pretreated with rapamycin (Rap, 0.2 μg/ml) for 48 h, followed by exposure to Cd (20 μM) for 4 h (for Western blotting) or 24 h (for cell morphology, live cell assay and DAPI staining). A) Total cell lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis using indicated antibodies. The blots were probed for β-tubulin as a loading control. Similar results were observed in at least three independent experiments. B and C) Silencing S6K1 enhanced preventive effect of rapamycin on Cd-induced B) cell viability reduction and C) apoptosis in PC12 and SH-SY5Y cells. Results are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 5). a p < 0.05, difference with control group; b p < 0.05, S6K1 shRNA group versus GFP shRNA group.