Figure 1.
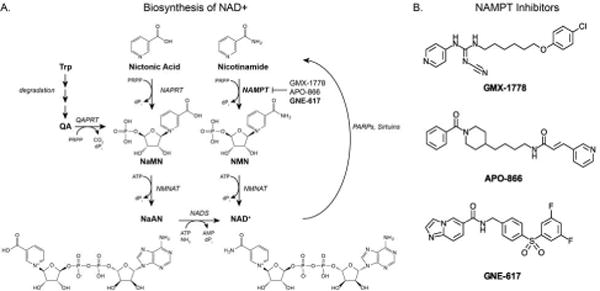
(A) NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is synthesized via a number of pathways. Both Nicotinic acid and Nicotinamide can be converted to NAD. Additionally, when tryptophan (Trp) is degraded, quinolinic acid (QA) is enzymatically converted to nicotinic acid mononucleotide (NaMN) and subsequently nicotinic acid adenine dinucleotide (NaAD) and later NAD. Due to increased activity of PARPs, Sirtuins, etc…NAD+ is consumed with nicotinamide as a product. (B) NAMPT inhibitors. GMX-1776 (CHS-828) is a pyridly cyanoguanidine NAMPT inhibitor that also inhibits the NF-kB pathway(42). APO-866 (Daporinad or FK866) is another NAMPT inhibitor, which also potentially inhibits VEGF(43). GNE-617 is a recently developed amide-containing inhibitor(11).
Abbreviations: NaMN – nicotinic acid mononucleotide, NMN – nicotinamide mononucleotide, NAPRT – nicotinate phosphoribosyltransferase (EC 2.4.2.11), QAPRT – quinolate phosphoribosyltransferase (EC 2.4.2.19), NMNAT – nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyl-transferase (EC 2.7.7.1), NAMPT – nicotinamide phosphoribosyltransferase (EC 2.4.2.12), NADS – NAD+ synthetase (EC 6.3.1.5), PRPP – 5-phospho-alpha-D-ribose 1-diphosphate dPi – diphosphate
