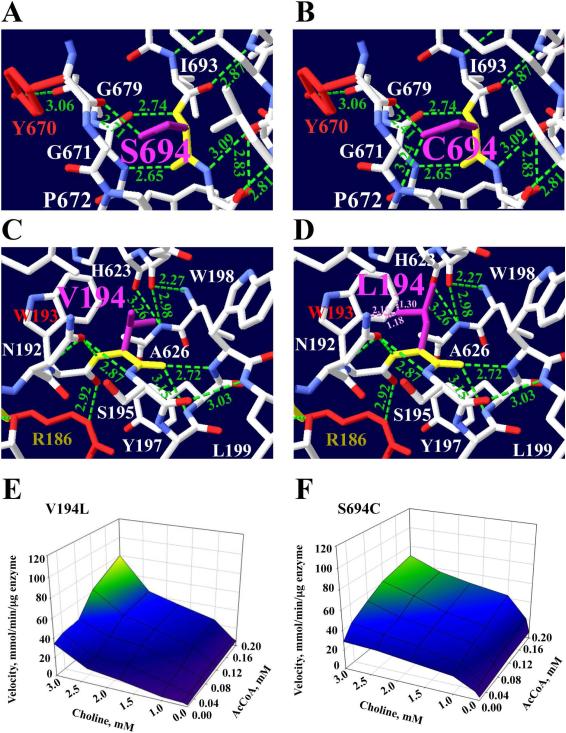
Fig 5.
Mutations p.Ser694Cys and p.Val194Leu affect substrate binding site. The structure shows interactions with residues that are close to Ser694 or Val194. a Ser694 forms H-bonds with Ser694 backbone, Gly679 amino group, Gly679 and Tyr670 (red) backbone. b The mutated residue was best accommodated by rotamer #3. The Ser694 (105 Da) with a small polar hydroxyl side chain changes to Cys694 (121 Da), which has a larger hydrophobic side chain. The mutation forms a new H-bond between the Cys694 side chain NH2 group and the Pro672 amino group. c The p.Val194Leu mutation is close to the acetyl-CoA binding site at α-helix 4. Val194 forms three H-bonds, with Ile559, Tyr197 and Asn192. The Val194 aliphatic side chain changes to Leu194 with a larger aliphatic side chain. d The mutated residue was best accommodated by rotamer #3. The Leu194 mutation creates clash interactions (pink dotted lines) with the Thr193 phenolic ring and with Asn192. e This mutation produces an increase of Km for choline by 1.4-fold, for AcCoA by 3.8-fold, and for Kcat by 2-fold. f The 3D kinetic graph shows a decrease of 48% for Kcat and a 2-fold increase in Km for choline. Cys694 has rotamer #3 with score of −4 and p= 22%. For Leu194 is rotamer #3 with a score of −4 and p = 40%