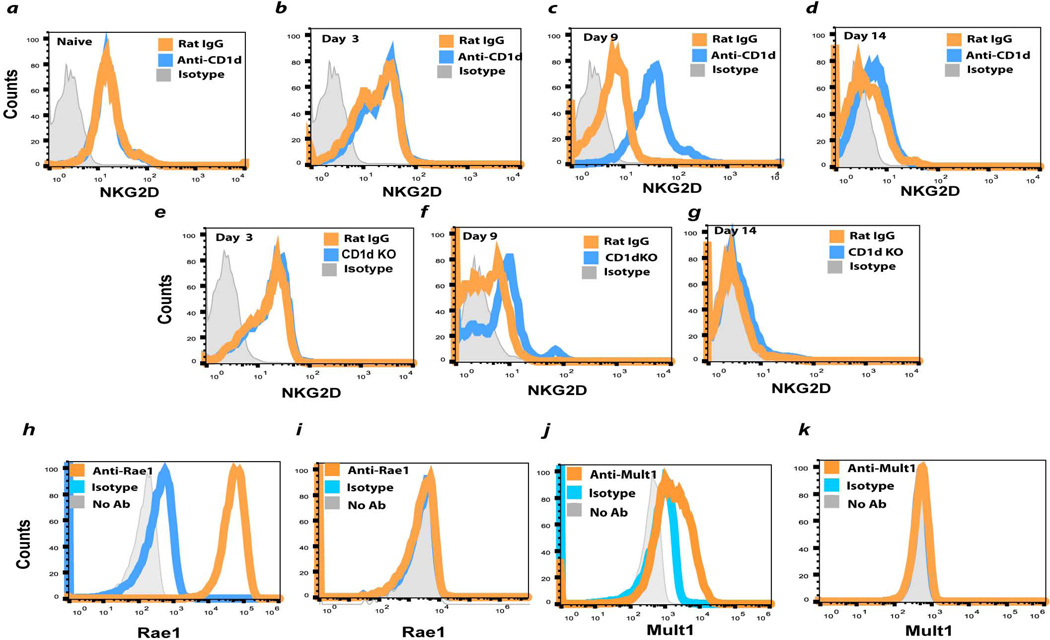
Figure 6.
Expression of NK cell activating receptor NKG2D on liver NK cells and NKG2D ligands of B16LS9 melanoma cells. Liver NK cells were assessed for surface expression of the NK cell activating receptor NKG2D: (a) Naive WT mice and WT mice treated with anti-CD1d or isotype control antibody and tested (b) 3, (c) 9, or (d) 14 days after intrasplenic tumor injection or CD1d KO mice tested (e) 3(f) 9, or (g) 14 days after intrasplenic tumor injection. Tumor cells were examined by flow cytometry for the expression of the NKG2 activating ligand Rae1 (h) Yac-1 lymphoma cells (positive control) or (i) B16LS9 melanoma cells. NKG2D ligand Mult1 was examined on (j) Yac-1 lymphoma cells (positive control) or (k) B16LS9 melanoma cells. The results shown here are from one of two independent experiments that produced similar results.