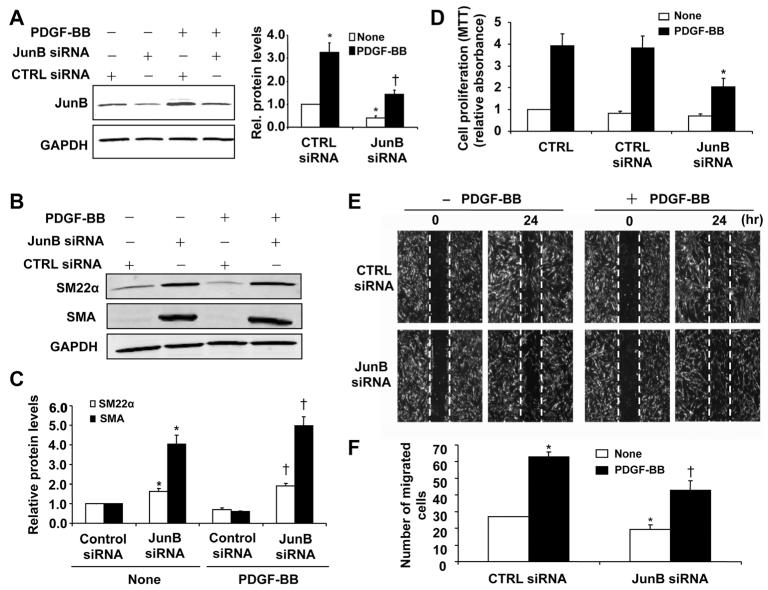
Figure 7. JunB is critically implicated in vascular smooth muscle cell (VSMC) proliferation and migration.
A, Silencing of JunB by specific small interfering RNA (JunB siRNA; 100 nmol/L) reduced JunB expression as determined by Western blot. *P<0.05 vs control (CTRL) siRNA without platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) treatment; †P<0.05 vs CTRL siRNA with PDGF (20 ng/mL) treatment. B, Silencing JunB increases the expression of SMC marker genes smooth muscle 22α (SM22α) and smooth muscle α-actin (SMA), as determined by Western blot analysis. C, Densitometric analysis of SM22α and SMA protein levels as measured by Western blot (n=5). *P<0.05 vs CTRL siRNA without PDGF treatment; †P<0.05 vs CTRL siRNA with PDGF (20 ng/mL) treatment. D, JunB knockdown attenuated PDGF-BB (20 ng/mL)-induced proliferation in human aortic SMCs as determined by MTT assay (n=4). *P<0.05 vs control siRNA with PDGF-BB treatment. E, VSMCs were transfected with JunB siRNA (100 nmol/L). Forty-eight hours after transfection, VSMCs were starved and cell migration was measured after PDGF-BB (20 ng/mL) stimulation for 24 h by scratch-wound assay. F, Quantitation of migrated cells. The data are means±SD of the number of migrated cells from 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05 vs CTRL siRNA without PDGF treatment; †P<0.05 vs CTRL siRNA with PDGF treatment.