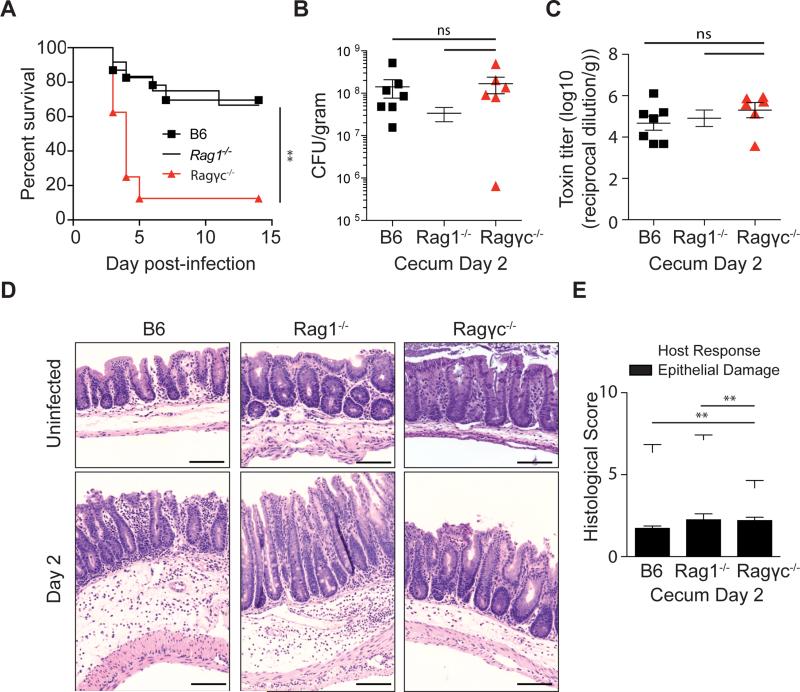
Figure 1. Absence of innate lymphoid cells leads to increased susceptibility to C. difficile.
(A) C57BL/6, Rag1−/−, Ragγc−/− mice were inoculated with 200 spores of C. difficile (VPI 10463 strain) and were assessed for survival following infection. Survival curve is a combination of 5 independent experiments (C57BL/6 n=23, Rag1−/− n=12, Ragγc−/− n=8). At day 2 post-infection (B) C. difficile burden and (C) toxin levels were measured from the cecal content. (D) Representative H&E stained cecal sections from antibiotic-treated, uninfected and day 2 infected C57BL/6, Rag1−/−, Ragγc−/− mice. Scale bar = 100μm. (E) Pathology score of histological tissue sections based on cellular infiltration/edema (host response), and epithelial layer degeneration (n=9-11). *p<0.05, **p<0.01. ns = not significant. Data shown are mean ± SEM. See also Figure S1 and S2.