Figure 2. Shared Decision Making in Goals of Care Discussions.
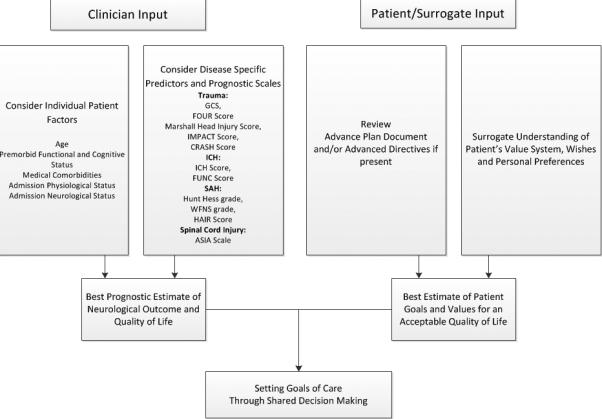
Both physicians and the patient/surrogate contribute to goals of care discussions. The physician should consider how individual patient factors and published prognostic scales contribute to the patient's overall prognosis. The patient/surrogate should contemplate the patient's advance directive and value system to determine if the best estimated prognosis is aligned with the patient's perception of an acceptable quality of life. Based on this balance, a shared-decision for appropriate goals of care can be reached.
GCS=Glasgow Coma Score[17]; FOUR Score[90]; Marshall Head Injury Score[91]; IMPACT score[92]; CRASH score [93]; ICH=intracerebral hemorrhage; ICH Score[18]; FUNC Score[21]; SAH=subarachnoid hemorrhage; Hunt Hess grade[20]; WFNS=World Federation of Neurosurgeons Score[94]; HAIR score[95]; ASIA= American Spinal Injury Association Scale[96]
