Figure 6.
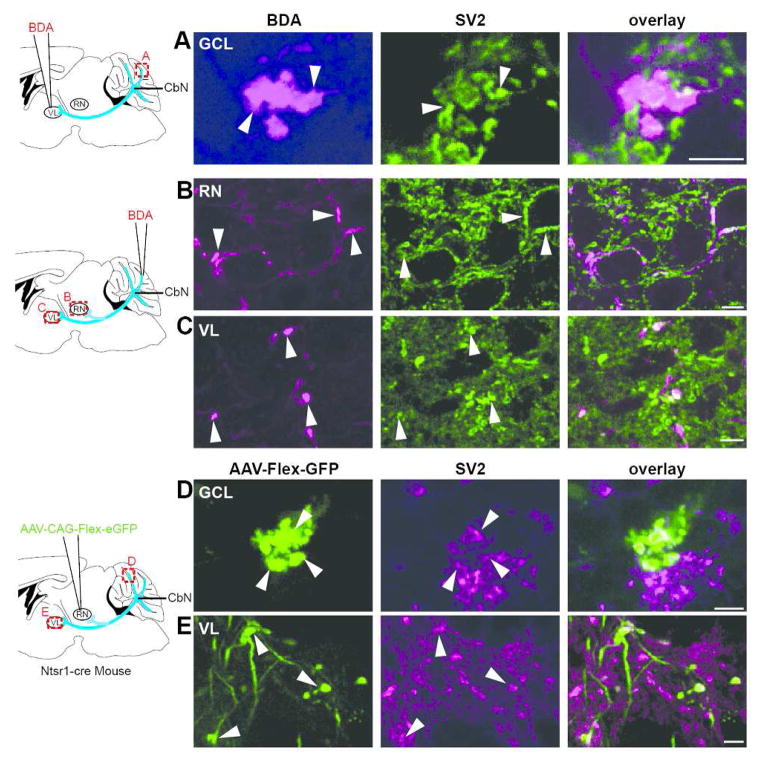
BDA- and virally- labeled boutons are immunopositive for SV2. A. (far left) A schematic diagram illustrating site of BDA injection to the ventrolateral thalamus (VL) is shown; (left) A cerebellar mossy fiber rosette located in the Crus I lobule labeled with BDA after a VL injection was immunopositive for SV2 (middle) as shown in the overlay (right; n=3). Confocal stack thickness was 1.35 μm. B–C. (far left) Schematic diagram of site of BDA injections into the granule cell layer. (See text for the range of injection sites for these experiments.) (left) Terminal boutons labeled with BDA in the red nucleus (RN) after a granule cell layer injection at the base of the Simple lobule near the primary fissure (n=5) expressed SV2 (middle) as shown in the overlay (right). Confocal stack thickness was 1.7 μm. C. (left) BDA-labeled terminal boutons were observed in VL following granule cell layer injection at the base of the Simple lobule near the primary fissure (n=5); SV2 immunostaining (middle) overlayed with labeled terminal (right). Confocal stack thickness was 0.34 μm. D–E. D. (far left) A schematic of AAV1-CAG-Flex-eGFP injection into the red nucleus of Ntsr1-Cre mice is shown. (left) Terminal boutons labeled with GFP were observed in the granule cell layer of the 4/5 lobule following virus injections into the RN of Ntsr1-Cre mice (n=5); these terminals expressed SV2 (middle) as shown in overlay (right). Confocal stack thickness was 1.89 μm. E. (left) GFP-expressing terminal boutons were seen in VL following viral injections to the RN of Ntsr1-Cre mice (n=5); SV2 immunostaining (middle) is overlayed with boutons (right). Confocal stack thickness was 1.62 μm. Scales, A,D = 5 μm; B,C and E = 10 μm.