Figure 1.
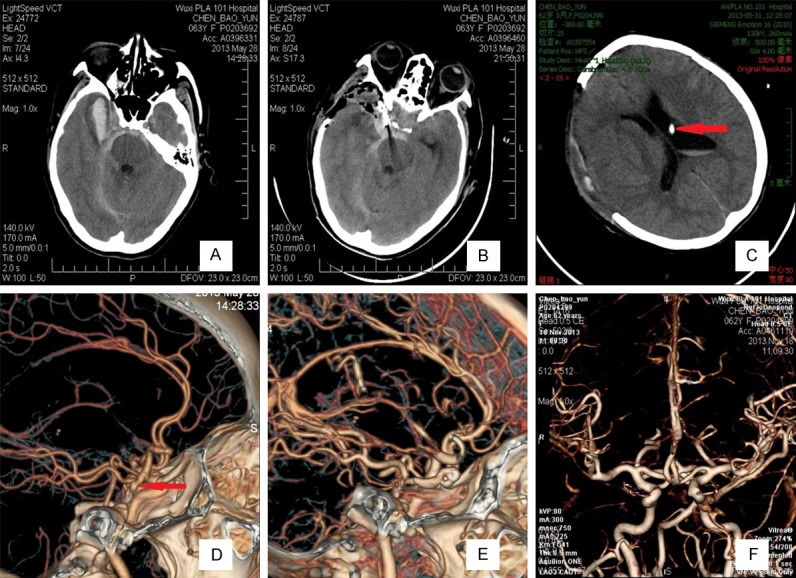
Images obtained from the 60 patients who were assessed at a Hunt-Hess grade V and Fisher grade 3 before undergoing ultra-early microsurgery combined with extraventricular drainage. After a 14-month follow-up, their Glasgow Outcome Scale was 5. A. A CT scan showed extensive SAH (especially at the basal cistern) and right temporal frontal lobe intracerebral hematoma. B. A postoperative CT scan showed that the aneurysm was occluded and that the hematoma was sufficiently removed. C. Three days postoperatively, a CT scan showed that the ventricle was normal. Red arrows indicate that the extraventricular drainage tube in the ventricle. D. Computed tomography angiography (CTA) showed right posterior communicating aneurysms, and red arrows indicate the aneurysm. E. Computed tomography angiography (CTA) after ultra-early microsurgical treatment showing that the aneurysm was perfectly occluded. F. Six months postoperatively, CTA showed no obvious intracranial vascular stenosis and normal vascular morphology.
