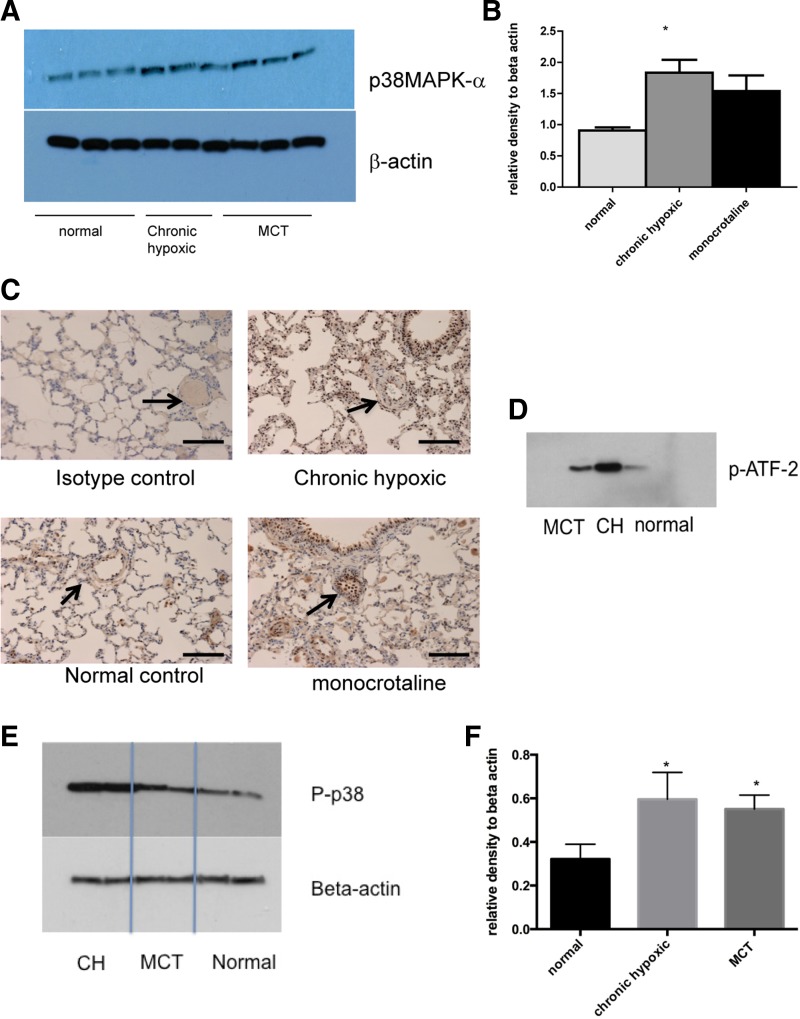
Fig. 2.
Increased expression of p38 MAPK α-isoform in animal models of PH. A: lungs from normal, CH, and MCT animals were harvested and homogenized with a cocktail of phosphatase and kinase inhibitors. The protein concentration was quantified using the BCA method. Equal concentrations were then loaded on a gel and blotted for p38 MAPKα and β-actin for loading control. There are 3 wells for each condition. Immunoblot shown is best representative of 3 experiments using 3 different animals with each condition. B: densitometry of immunoblot in A. Values are mean arbitrary values from 3 immunoblots expressed relative to the value for β-actin. *P < 0.05 by ANOVA. C: lung sections (5 mm) were prepared from normal, CH, and MCT animals. Sections were stained for p38 MAPKα using 1:400 dilution. Magnification: ×20. Bar represents = 150 mm. Arrows identify blood vessels. D: lungs from normal, CH, and MCT animals were harvested and homogenized with a cocktail of phosphatase and kinase inhibitors. The protein concentration was quantified using BCA method. Equal concentrations were then used in a p38 MAPK activity assay using immunoprecipitation and the phosphorylation of activating transcription factor-2 (ATF-2) as a read out. Immunoblot shown is representative of 3 experiments using 3 different animals. E and F: lungs from normal, CH, and MCT animals were harvested and homogenized with a cocktail of phosphatase and kinase inhibitors. The protein concentration was quantified using BCA method. Equal concentrations were then loaded on a gel and blotted for phosphorylated p38 MAPK and β-actin for loading control. Immunoblot shown is representative of 3 experiments using 3 different animals with each condition. Densitometry is shown for remaining blots. *P < 0.05.