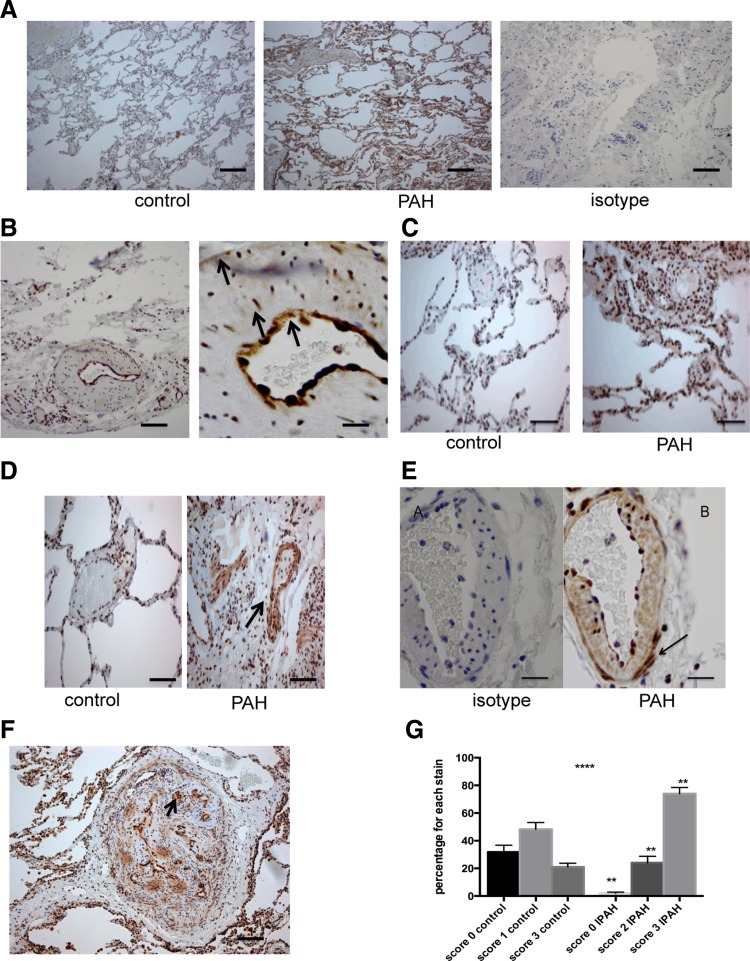
Fig. 8.
Phospho-p38 MAPK and p38 MAPKα expression in explanted lungs from patients with idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension (IPAH). A: sections of 5 mm were taken. Then, normal control lung and IPAH lung are stained for phospho-p38 MAPK at dilution of 1:300. The isotype on IPAH lung is also shown. This dilution was optimally assessed for. Objective: ×20. Bar = 150 mm. B: high-power microscopy shows that there is strong staining for phospho-p38 MAPK in the intima, media, and the adventitia (arrows). Objective lens: ×20 and ×40. Bar = 50 mm. C: sections of control lung (A) and IPAH lung (B) were stained for p38 MAPKα at dilution of 1:300. Objective lens × 20. Bar = 150 mm. D: staining for p38 MAPKa showed increased cytosolic staining in the IPAH lung (right) compared with control lung (left). E: high-power view (×40) of staining with isotype and p38 MAPKα in a vessel in IPAH lung. This shows staining throughout the vessel layers but especially in adventitia and fibroblast cells (arrow). Bar = 50 mm. F: low-power view of a plexiform lesion. Staining for p38 MAPKα using 1:300 dilution. Objective lens × 20. Bar = 150 mm. G: histological scoring shows increased p38 MAPKα staining throughout the vascular wall. With the use of a well-validated histological scoring system (Allred), the vascular wall cells were scored for intensity of staining. The intensity multiplied by the number of vessels with that intensity determines the values. Values shown are from 5 random high-power fields from 2 slides. ****P < 0.0001 by ANOVA. **P < 0.001 for individual IPAH vs. control columns.