Figure 1.
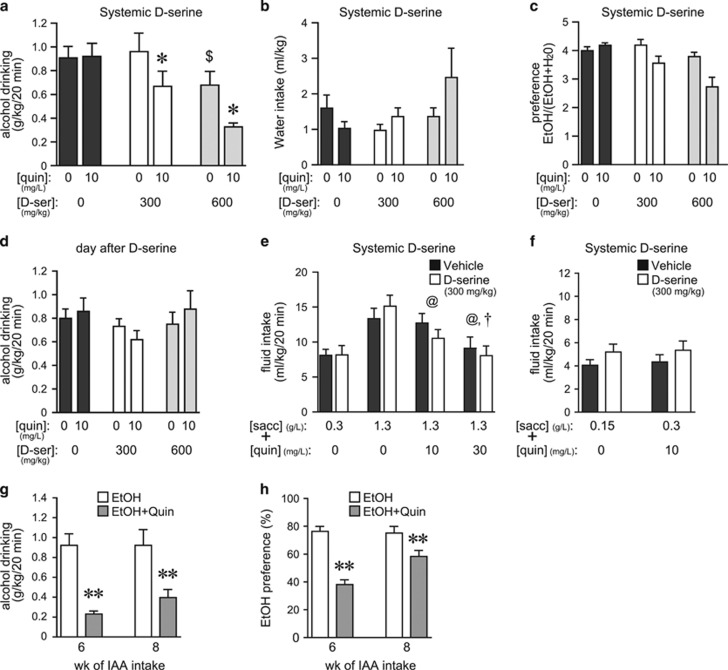
Systemic D-serine only reduced aversion-resistant alcohol consumption. (a) D-serine (i.p., 300 mg/kg) reduced drinking of quinine-adulterated alcohol but not quinine-free alcohol (quinine: F1, 7=20.675, p=0.003; D-serine: F1, 14=17.799, p=0.001; interaction: F1, 14=4.294, p=0.035). *p<0.05 for quinine/D-serine-300 vs quinine/vehicle (n=8). D-serine at 600 mg/kg reduced intake of both quinine-adulterated and quinine-free alcohol (*p<0.05 quinine-free vs quinine conditions; $p<0.05 D-serine vs vehicle). (b, c) D-serine decreases in quinine-adulterated alcohol drinking were not accompanied by changes in water intake (b) (quinine: F1, 7=1.926, p=0.208; D-serine: F1, 14=1.210, p=0.327; interaction: F1, 14=3.268, p=0.068) but there were significant decreases in preference (alcohol intake/(alcohol+water intake)) (c) (quinine: F1, 7=13.862, p=0.007; D-serine: F1, 14=12.561, p<0.001; interaction: F1, 14=3.313, p=0.066). (d) D-serine treatment did not reduce alcohol intake the day after D-serine treatment (quinine: F1, 7=0.099, p=0.763; D-serine: F1, 14=1.589, p=0.239; interaction: F1, 14=1.194, p=0.332). (e) D-serine (300 mg/kg) did not alter intake of saccharin±quinine (n=13; saccharin–quinine doses: F3, 36=27.837, p<0.001; D-serine: F1, 36=0.213, p=0.653; interaction: F3, 36=2.074, p=0.121). Quinine significantly reduced intake of 1330 g/l saccharin (@p<0.01, sacc with vs without quin; †p<0.01, sacc with 10 vs 30 mg/l quin). (f) D-serine (300 mg/kg) did not reduce, but instead slightly increased, consumption of lower saccharin concentrations (150 mg/l) or saccharin–quinine (300 mg/l sacc+10 mg/l quin) (n=14; saccharin±quinine: F1, 13=0.641, p=0.770; D-serine: F1, 13=13.886, p=0.003; interaction: F1, 13=0.035, p=0.854). (g, h) After only 6 or 8 weeks of intermittent alcohol intake (n=17), quinine adulteration (30 mg/l) significantly reduced alcohol intake (g) (±quinine: F1, 16=26.727, p<0.001) and preference (h) (±quinine: F1, 16=43.911, p<0.001) (see also Hopf et al, 2010), whereas quinine adulteration did not reduce alcohol intake after >12 weeks of intermittent intake (a). **p<0.01. Sacc, saccharin; D-ser, D-serine; quin, quinine; veh, vehicle.