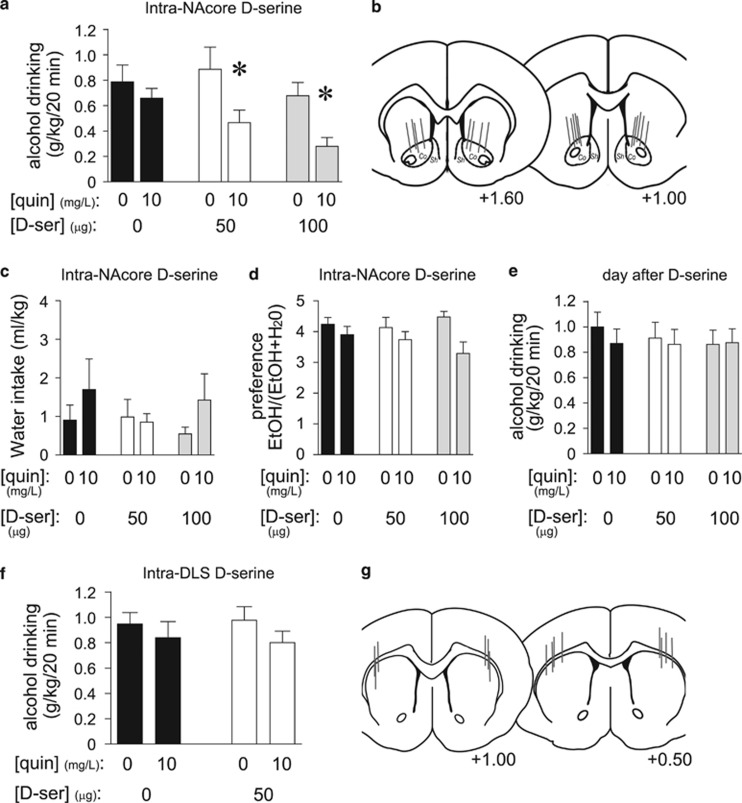
Figure 2.
D-serine within the NAcore reduced aversion-resistant alcohol intake. (a) Infusion of D-serine within the NAcore (50 or 100 μg/side) significantly reduced consumption of quinine-adulterated alcohol but not quinine-free alcohol (n=9) (quinine: F1, 16=13.761, p=0.006; D-serine: F2, 16=7.543, p=0.005; interaction: F2, 16=3.917, p=0.041). *p<0.05 for no quinine vs quinine conditions. (b) Histological placement of cannulae targeting the NAcore. Co, NAcore; Sh, NAcb shell. (c, d) Decreased quinine-adulterated alcohol drinking was not accompanied by changes in water intake (c) (all p>0.1) or alcohol preference (d), although quinine did decrease preference (quinine: F1, 16=13.275, p=0.007; D-serine: F2, 16=0.444, p=0.788; interaction: F2, 16=2.173, p=0.146). (e) Intra-NAcore D-serine did not reduce alcohol intake the day after D-serine treatment (all p>0.3). (f) Infusion of D-serine within the DLS (50 μg/side) had no impact on quinine-free or quinine-adulterated alcohol intake (n=8) (all p>0.15). (g) Histology of cannulae targeting the DLS. Numbers in (b) and (g) indicate distance from Bregma. D-ser, D-serine; veh, vehicle.