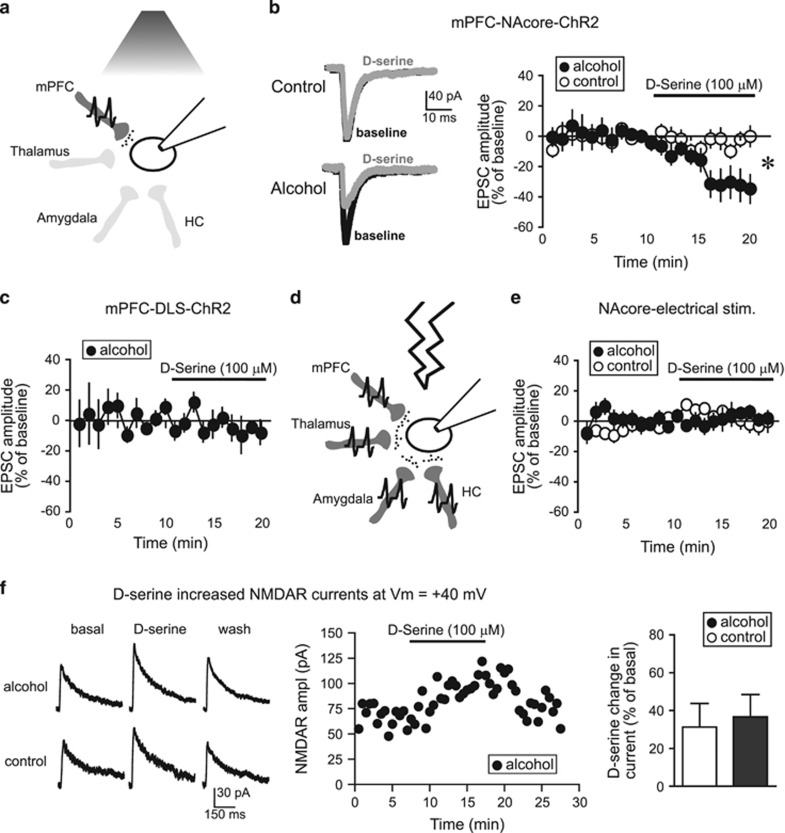
Figure 3.
D-serine inhibited EPSCs evoked at −70 mV under mPFC-NAcore terminals in alcohol-drinking rats. (a) Cartoon showing that a 480 nm LED only evoked glutamate release (small black circles) from ChR2-filled mPFC terminals within the NAcore (dark gray). HC, hippocampus. (b) Sample traces and grouped data demonstrating that D-serine (100 μM) significantly reduced mPFC-ChR2-evoked EPSCs at −70 mV in neurons from alcohol-drinking rats (n=9; −32.9±10.1% vs baseline) but not naive rats (n=8; −4.0±4.2% vs baseline). Mann–Whitney test, U=10; p=0.011 alcohol vs control, *p<0.05 alcohol vs control. (c) D-serine (100 μM) did not reduce mPFC-evoked EPSCs at −70 mV in the DLS of alcohol drinkers (n=5; −7.4±6.2% vs baseline, t4=1.345, p=0.250 paired t-test). (d) Cartoon showing that electrical stimulation (lightning) evoked glutamate release (small black circles) from terminals originating from all regions (dark gray); only some of the known glutamate inputs to NAcore (Gerfen, 2004) are shown. (e) D-serine did not reduce electrically evoked EPSCs at −70 mV in NAcore neurons from alcohol-drinking (n=6; 3.0±3.3% vs baseline) or control rats (n=9; −1.8±5.5% vs baseline). (f) D-serine enhanced NAcore NMDARs evoked at +40 mV, with no difference between alcohol and control (n=4 alcohol, 4 control; t6=0.313, p=0.765). Ampl, amplitude.