Figure 5.
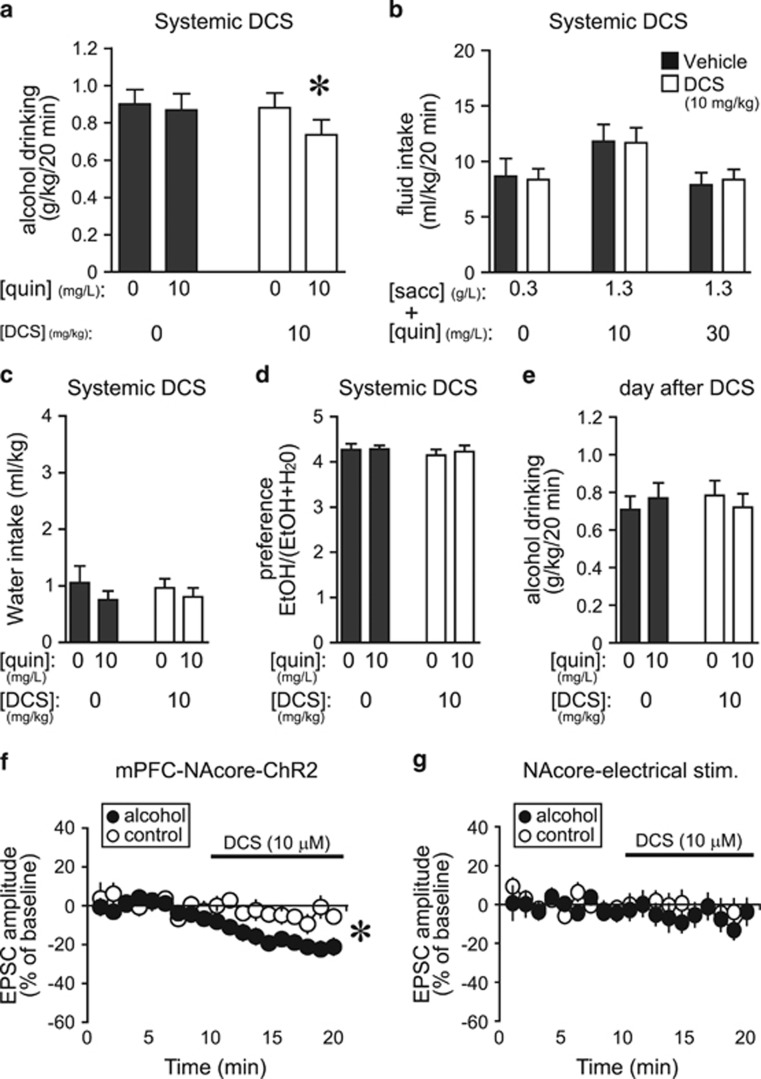
D-cycloserine reduced aversion-resistant alcohol intake and EPSCs evoked at −70 mV in vitro under mPFC-NAcore terminals. (a) DCS (i.p., 10 mg/kg) reduced drinking of quinine-adulterated alcohol but not quinine-free alcohol (n=13; quinine: F1, 12=3.501, p=0.086; D-serine: F1, 12=1.62, p=0.162; interaction: F1, 12=4.811, p=0.049). *p<0.05 for DCS vs all other conditions. (b) Systemic DCS did not alter intake of saccharin±quinine (n=14; saccharin–quinine doses: F2, 26=5.78, p=0.008; D-serine: F1, 26=0.001, p=0.996; interaction: F2, 26=0.088, p=0.916). (c–e) DCS reduction of aversion-resistant drinking was not accompanied by changes in concurrent water intake (c) (all p>0.1), alcohol preference (d) (all p>0.4), or alcohol intake the next day (e) (all p>0.7). (f) DCS (10 μM) significantly reduced mPFC-ChR2-evoked EPSCs at −70 mV in neurons from alcohol-drinking rats (n=12; −21.6±3.8% vs baseline) but not naive rats (n=9; −5.2±3.8% vs baseline). *p<0.05 alcohol vs control. (g) DCS did not reduce electrically evoked EPSCs at −70 mV in NAcore neurons from alcohol-drinking (n=7; −8.1±5.5% vs baseline) or control rats (n=14;−3.8±6.4% vs baseline). Veh, vehicle.