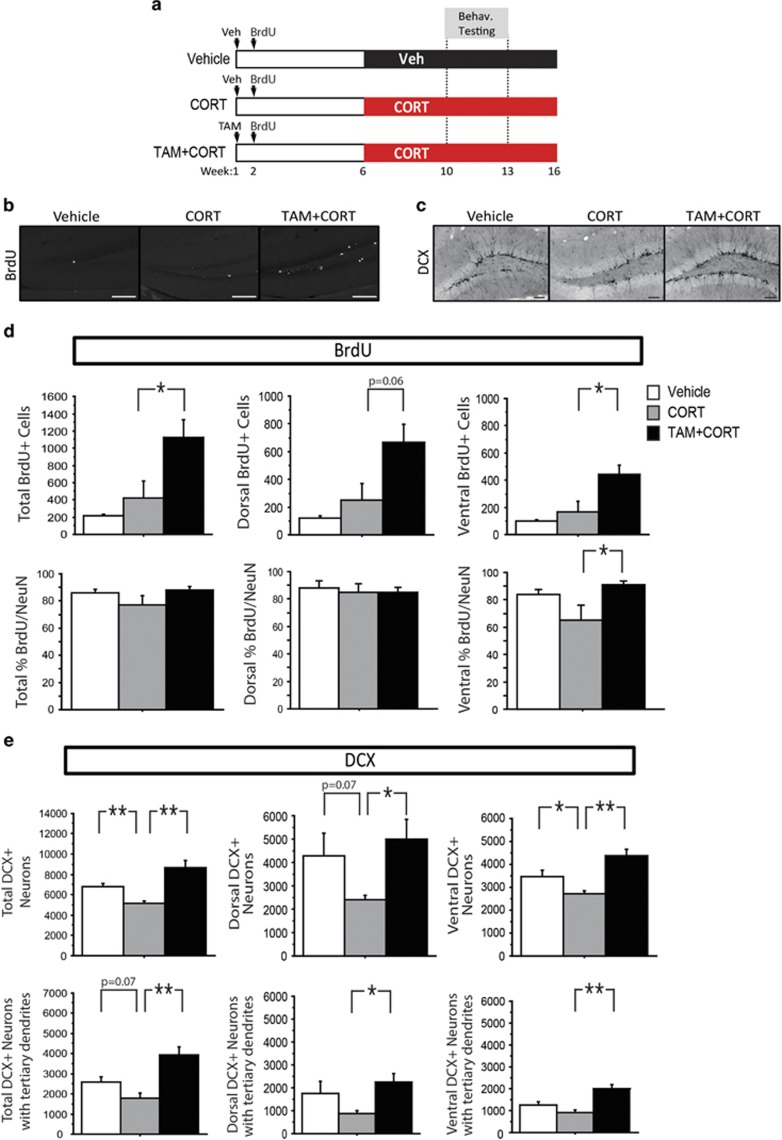
Figure 3.
Genetic ablation of Bax in neural stem cells and progenitors protects against chronic CORT-induced reduction in adult hippocampal neurogenesis. (a) Experimental timeline: iBax mice were injected with either vehicle or TAM. Six weeks later, mice received vehicle or CORT via drinking water for the remainder of the experiment. Three behavioral groups were tested, vehicle (top line), CORT alone (middle line), and TAM+CORT (bottom line). (b and c) Representative images of BrdU and DCX in the dentate gyrus (scale bars 100 um). (d) While no significant difference in the number of BrdU-positive cells is observed between vehicle- and CORT-treated mice (P>0.05), TAM+CORT treatment increases the number of BrdU-positive cells (P=0.046) (dorsal P=0.064; ventral P=0.027). The majority of BrdU-labeled cells are colabeled with the mature neuronal marker NeuN. The percent of BrdU-labeled cells colabeled with NeuN is the same between all groups in the dorsal dentate gyrus. In the ventral dentate gyrus, a lower percentage of BrdU-positive cells are colabeled with NeuN in CORT-treated mice, compared with those treated with TAM+CORT (P=0.022). (e) CORT treatment decreases the total number of DCX-positive neurons (P=0.005), and there is a trend for a decrease in the number of DCX-positive neurons with tertiary dendrites (P=0.07). TAM+CORT prevents these effects (P=0.002 for total DCX-positive neurons; P=0.002 for DCX-positive neurons with tertiary dendrites). In the dorsal and ventral subregions, the total number of DCX-positive neurons is decreased by CORT (dorsal P=0.07; ventral P=0.039), and rescued in TAM+CORT-treated mice (dorsal P=0.028; ventral P=0.002); the number of DCX-positive neurons with tertiary dendrites is increased in TAM+CORT-treated mice compared with mice treated with CORT alone (dorsal P=0.013; ventral P=0.001). n=4–7/group in all analyses. All error bars represent SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. BrdU, bromodeoxyuridine; CORT, corticosterone; DCX, doublecortin; NeuN, neuronal nuclei; TAM, Tamoxifen.