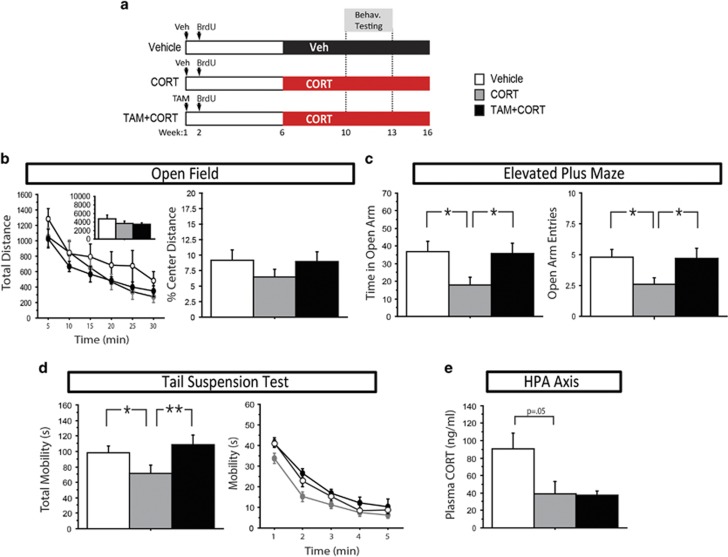
Figure 4.
Genetically increasing adult hippocampal neurogenesis in iBax mice prevents the effects of chronic CORT on mood-related behavior, but does not affect HPA axis regulation. (a) Experimental timeline. (b) No statistically significant differences were seen between groups in total distance or percent center distance in the open field test (P>0.05). n=8–10/group. (c) In the elevated plus maze, CORT-treated mice spent significantly less time in the open arms (P=0.015) and had fewer open arm entries (P=0.017) than controls. These effects were reversed in TAM+CORT-treated mice (P=0.018 for open arm time, P=0.049 for open arm entries). n=12–15/group. (d) In the tail suspension test, CORT-treated mice displayed decreased mobility (P=0.032), which was reversed in TAM+CORT-treated mice (P=0.005). In the line graph, data is represented in 1-min bins for the duration of the test. n=14–15/group. (e) Trunk blood was collected 5 min after a 1-min swim stress, from which plasma was isolated. There is a strong trend for CORT-treated mice to have lower plasma CORT levels than controls following forced swim stress (P=0.05), but no difference between CORT and TAM+CORT groups (P=0.91). n=5–6 group. All error bars represent SEM. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. CORT, corticosterone; HPA, hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal; TAM, Tamoxifen.