Table 1. Properties of the real-world networks studied in this work.
| Network | N | E | 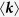 |
kmax | Hk | r | C | kSmax | λc | λ |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1133 | 5451 | 9.6 | 71 | 1.942 | 0.078 | 0.220 | 11 | 0.06 | 0.08 | |
| CA-Hep | 8638 | 24806 | 5.7 | 65 | 2.261 | 0.239 | 0.482 | 31 | 0.08 | 0.12 |
| Hamster | 2000 | 16097 | 16.1 | 273 | 2.719 | 0.023 | 0.540 | 24 | 0.02 | 0.04 |
| Blog | 3982 | 6803 | 3.4 | 189 | 4.038 | −0.133 | 0.284 | 7 | 0.08 | 0.27 |
| PGP | 10680 | 24340 | 4.6 | 206 | 4.153 | 0.240 | 0.266 | 31 | 0.06 | 0.19 |
| Astro | 14845 | 119652 | 16.1 | 360 | 2.820 | 0.228 | 0.670 | 56 | 0.02 | 0.05 |
| Router | 5022 | 6258 | 2.5 | 106 | 5.503 | −0.138 | 0.012 | 7 | 0.08 | 0.27 |
| Emailcontact | 12625 | 20362 | 3.2 | 576 | 34.249 | −0.387 | 0.109 | 23 | 0.01 | 0.10 |
| AS | 22963 | 48436 | 4.2 | 2390 | 61.978 | −0.198 | 0.230 | 25 | 0.004 | 0.13 |
Structural properties include number of nodes (N), number of edges (E), average degree 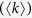 , maximum degree (kmax), degree heterogeneity (
, maximum degree (kmax), degree heterogeneity (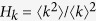 ), degree assortativity (r), clustering coefficient (C), maximum ks index (kSmax), epidemic threshold (λc), infection probability used in the SIR spreading in the main text (λ) (see Method for details). For the first six networks, there exist core-like groups. While for the last three networks, there is no core-like group in the network, which we will discuss in the last part.
), degree assortativity (r), clustering coefficient (C), maximum ks index (kSmax), epidemic threshold (λc), infection probability used in the SIR spreading in the main text (λ) (see Method for details). For the first six networks, there exist core-like groups. While for the last three networks, there is no core-like group in the network, which we will discuss in the last part.
