Figure 2.
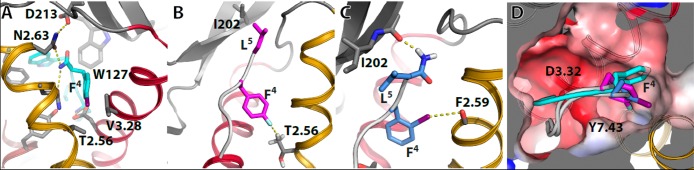
Computational models of the complexes between halogenated Endo-1 and Leu-ENK peptides in complex with μ- and δ1b-opioid receptors. (A) [4-I-Phe4]Endo-1 (in cyan) in complex with μ-OR. Phe4 is placed in a small cavity formed by Thr2.56 and Val3.28, making halogenation (iodine is shown) at the para position repulsive (steric hindrance). (B) [4-F-Phe4]Leu-ENK (in magenta) in complex with δ1b-OR. The negative electrostatic potential of fluorine forms a F···H–C hydrogen bond with the methyl group of Thr2.56. (C) [2-I-Phe4]-Leu-ENK-1 (in light blue) in complex with δ1b-OR. The positive σ-hole of iodine forms a halogen bond with the backbone carbonyl oxygen of Phe2.59. (D) The orientation of Phe4 in Endo-1 (cyan sticks), [4-F-Phe4]Leu-ENK (magenta), and [2-I-Phe4]Leu-ENK (light blue) inside the small cavity located between TMs 2 and 7. The negatively charged area (red) created by Asp3.32 is shown. The color code of the helices is TMs 1 in white, 2 in yellow, 3 in red, 4 in gray, 5 in green, 6 in blue, and 7 in brown.
