FIG 2.
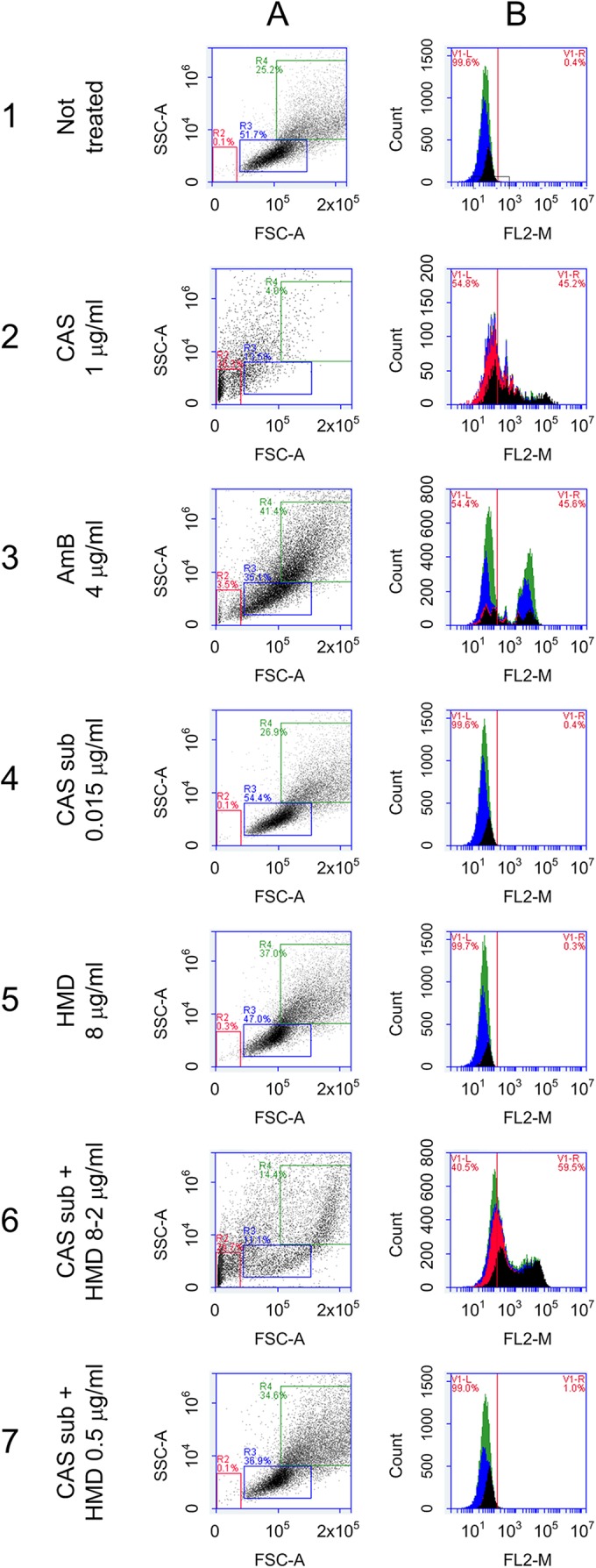
Flow cytometry assays with C. albicans to determine cellular viability by changes in membrane permeability using PI as a probe. The assays were performed with C. albicans and demonstrated that neither the sublethal dose of CAS nor the compound humidimycin itself (used at concentrations below 8 μg/ml) affected the cellular viability. (A) Normal population; (B) background of fluorescence emitted. (1) Nontreated cells. (2) Cells treated with 1 μg/ml of CAS (panel A shows the damaged population and panel B confirmed that PI was able to enter into the cell). (3) Cells treated with amphotericin B (AmB) at 4 μg/ml used as a control. (4) Cells treated with a sublethal dose (sub) of CAS (0.015 μg/ml) (panels A and B) presented the same profile as the nontreated cells (healthy cells). (5) Cells treated with 8 μg/ml of humidimycin (HMD) were also not affected. (6) Cells treated with a sublethal dose of CAS plus humidimycin at concentrations from 8 to 2 μg/ml presented the same damage profile as cells treated with 1 μg/ml of CAS (2). (7) Cells treated with a sublethal dose of CAS + humidimycin at concentrations of <2 μg/ml were not affected.
