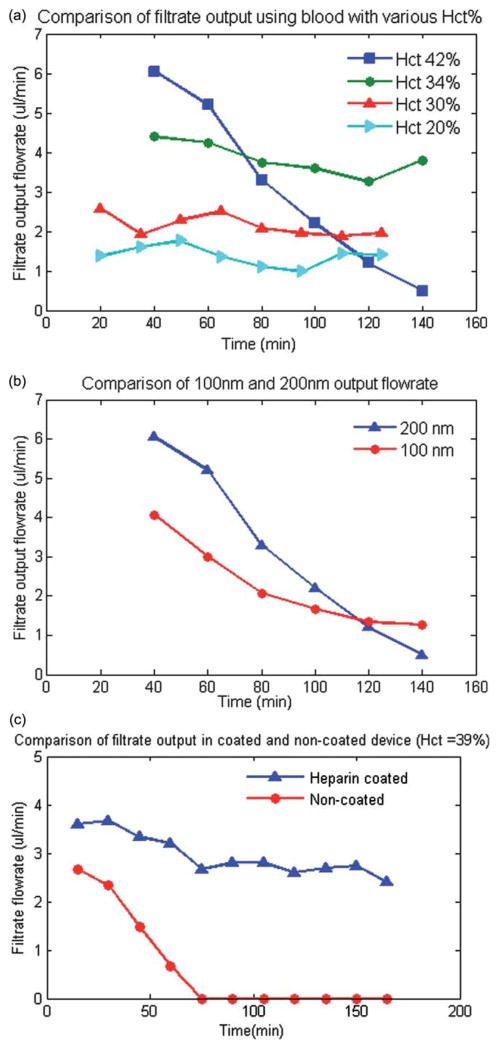
Fig. 3.
(a) A comparison of the experimental results of the total plasma separation flow rate with respect to blood inlet hematocrit level. The results indicate that initial filtration flow rate is higher for high level of hematocrit (42%) but it decreases rapidly due to accumulations of RBCs or platelet at the surface of the membrane. (b) A comparison of the plasma separation flow rate for 100 nm and 200 nm pore size membrane. The results indicates that the plasma flow rate is higher for 200 nm membrane. However, the flow rate decreases more rapidly over time for 200 nm membrane at hematocrit levels of 42%. (c) A comparison of the experimental results of the total plasma separation for anticoagulant coated and non-coated microdevice for blood Hct = 39% indicated that the filtration efficiency did not significantly decrease over time for the heparin pre-coated device but it decreased significantly for the non-coated device.