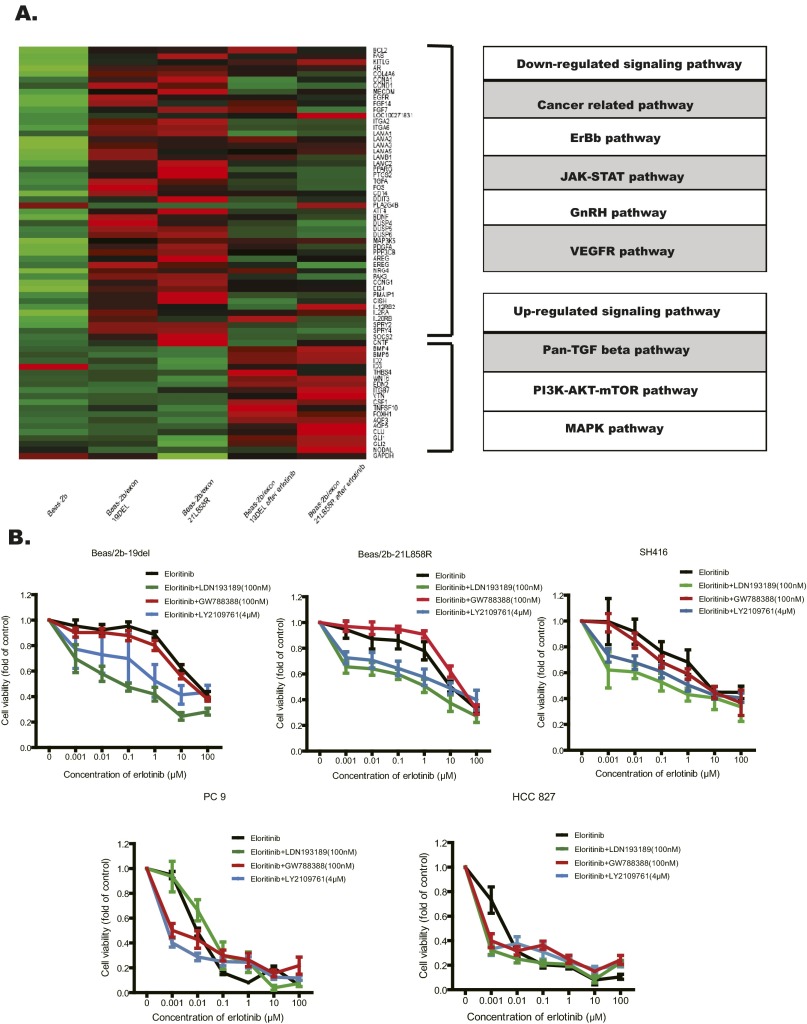
Fig. S4.
Activation of the BMP-BMPR-Smad1/5-70S6K pathway conferred resistance to EGFR-TKIs in lung SqCC cells and patients with EGFR mutations. (A) Total RNA was extracted from the indicated cells (Beas/2b, Beas/2b-19del, Beas/2b-21L858R cells, and also the treated Beas/2b-19del and Beas/2b-21L858R after 24 h of erlotinib) and analyzed with RNA-seq. Genes with expression up-regulated by more than 2.5-fold were screened out and for further signaling pathway match. (B) Cell viability analyses showed that combining erlotinib treatment with BMPR inhibitor (LDN193189), TGF-β inhibitor (GW788388), and pan-TGF-β inhibitor (LY2109761) overcame the EGFR-TKI resistance in lung SqCC cell lines (Beas/2b-19del, Beas/2b-21L858R, and SH416), but this was not effective in the lung adenocarcinoma cell lines (PC9 and HCC827). The drug concentrations were of the indicated doses. Viability at 72 h was calculated as the ratio of viable drug-exposed cells to viable DMSO-treated cells. (C) Cell viability analyses showed that knockdown via shRNA specific to BMPR-IA (shRNA-636) or BMPR-II (shRNA-1049), but not TGF-βR-II (shRNA-1515), improved sensitivity to erlotinib in both Beas/2b-19del cells and Beas/2b-21L858R cells. Viability at 72 h was calculated as the ratio of viable erlotinib-exposed cells to viable DMSO-treated cells. Moreover, Beas/2b-19del cells were treated with indicated shRNA and/or erlotinib for 24 h. Cell extracts were immunoblotted to detect the indicated proteins. (D) Indicated cells were treated with indicated drug combinations for 24 h. Cell extracts were immunoblotted to detect the indicated proteins. (E) Diagrams showing the speculated mechanisms of erlotinib resistance in EGFR mutant lung SqCCs. The BMP2/4-BMPRII-Smad1/5-p70S6K pathway was bypass-activated following erlotinib treatment.