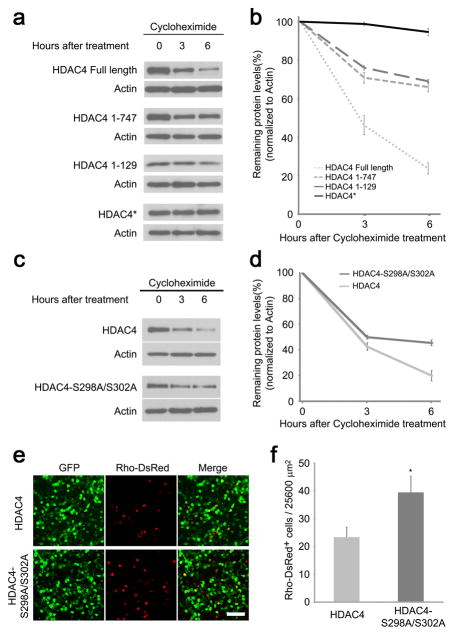
Figure 3.
Enhanced HDAC4 protein stability is correlated with greater rod protection efficiency. (a) Protein decay assay of HDAC4 Full Length and deletion alleles. HEK 293T cells were transfected with CAG-HDAC4 or CAG-HDAC4 deletion constructs for 20 hours before treatment with cycloheximide (100μg/ml) for 3 or 6 hours. Cell lysates were immunoblotted for HDAC4. The same immunoblot membranes were stripped and re-probed for actin. (b) Protein levels were quantified by densitometry after normalization to actin. Data are presented as mean ± s.d., n=3. (c) Protein decay assay for HDAC4 and HDAC4-S298A/S302A mutant. HEK293T cells were transfected with CAG-HDAC4 or CAG-HDAC4-S298A/S302A for 20 hours before treatment with cycloheximide (100μg/ml) for 3 or 6 hours. Cell lysates were immunoblotted for HDAC4. The same immunoblot membranes were stripped and re-probed for actin. (d) Protein levels were quantified by densitometry after normalization to actin. Data are presented as mean ± s.d., n=3. (e) HDAC4-S298A/S302A saved more rd1 rods in comparison to the wild type HDAC4 at P50. Scale bar, 40 μm. (f) Quantification of the preserved rods per 25600 μm2 on the flat-mount retina. *P<0.01. Data are presented as mean ± s.d., n=3.