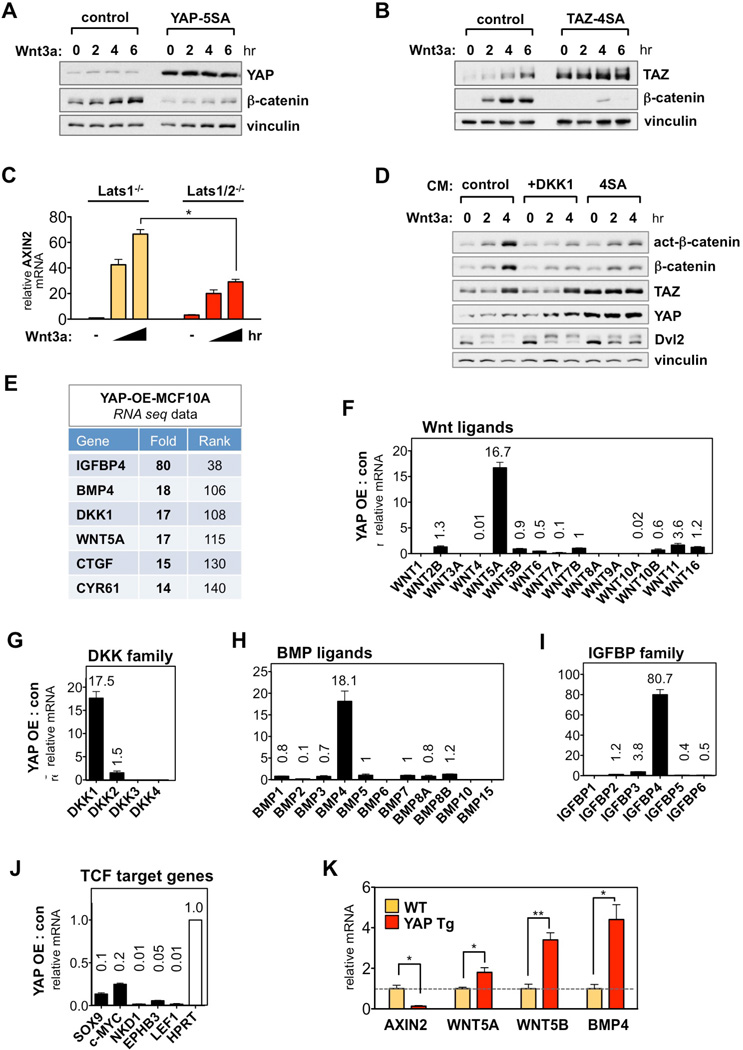
Figure 5. YAP/TAZ Induce Secreted Inhibitors of Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling.
(A and B) Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by nuclear YAP/TAZ. Stable MCF10A–YAP-5SA (A) and TAZ-4SA (B) cells were serum-starved, then stimulated with Wnt3a (100 ng/ml).
(C) Impaired Wnt/β-catenin signaling in Lats1/2 DKO cells. Axin2 mRNA level was measured in Wnt3a (100 ng/ml) stimulated Lats1 KO and Lats1/2 DKO MEFs. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05 (Student’s t-test).
(D) Inhibition of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by TAZ-4SA conditioned media. HEK293A cells were pretreated for 2 hr with conditioned media (CM) from control and TAZ-4SA-expressing MCF10A cells then stimulated with Wnt3a (100 ng/ml). In lanes 4–6, DKK1 (200 ng/ml) was added in control-CM.
(E) RNA-seq data in YAP-overexpressing (YAP-OE) MCF10A cells. The fold-induction of each gene is ranked among 22,341 genes.
(F-I) Induction of YAP target genes among the Wnt ligands (F), DKK family (G), BMP ligands (H), and IGFBP family (I). Fold-change by YAP is indicated above each bar graph. Ligands without corresponding number were undetectable or below threshold in RNA-seq analysis.
(J) Inhibition of β-catenin/TCF target genes by YAP.
(K) Induction of secreted Wnt inhibitors in YAP transgenic mouse liver. qRT-PCR analysis in the liver of YAP transgenic (YAP Tg) and control (WT) mice fed with 0.2 mg/ml doxycycline for 2 weeks. n = 3 mice per group; Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 (Student’s t-test).
See also Figure S5.