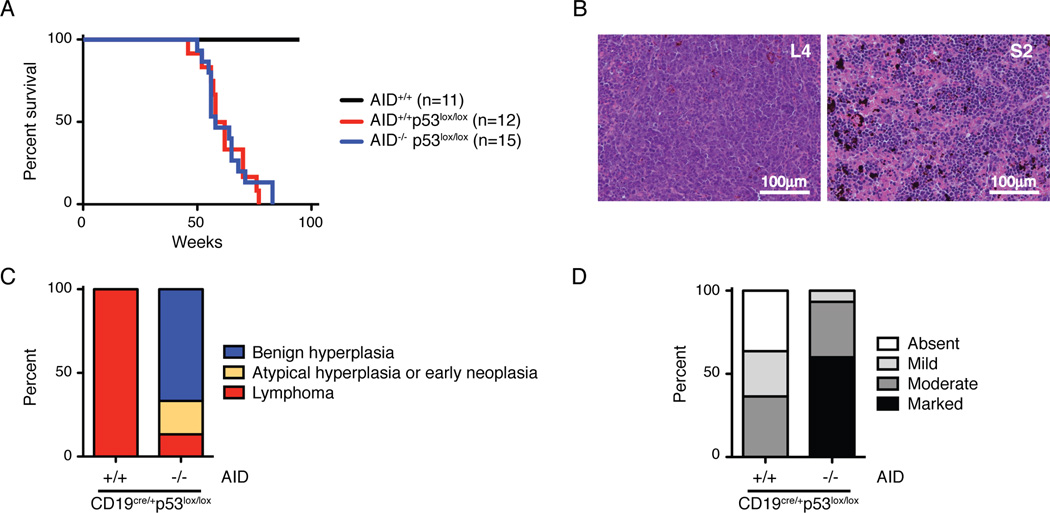
Figure 5. P53 suppresses and AID promotes Plasmodium induced lymphoma.
A- Survival of Plasmodium infected mice. All mice are also CD19cre/+.
B- Spleen histology of Plasmodium infected CD19cre/+p53lox/lox mice. L4 is AID proficient lymphoma and S2 is AID deficient benign B cell hyperplasia with marked extramedullary hematopoiesis.
C- Lymphoma versus benign hyperplasia in Plasmodium infected mice. Lymphoid tissues were evaluated by histology, immunohistochemistry, and flow cytometry. “Benign hyperplasia” indicates mice with splenomegaly but normal B cell distribution, with B220+ cells confined to follicular areas. “Atypical hyperplasia or early neoplasia” denotes splenomegaly and B220+ cells expanding into the periarteriolar lymphoid sheats (PALS). “Lymphoma” defines abnormal lymphoid tissue architecture and/or dissemination to multiple organs.
D- Extramedullary hematopoiesis in Plasmodium infected mice. Spleen sections were evaluated for the degree of extramedullary hematopoiesis.
See also Figure S5 and Table S2.