Figure 1.
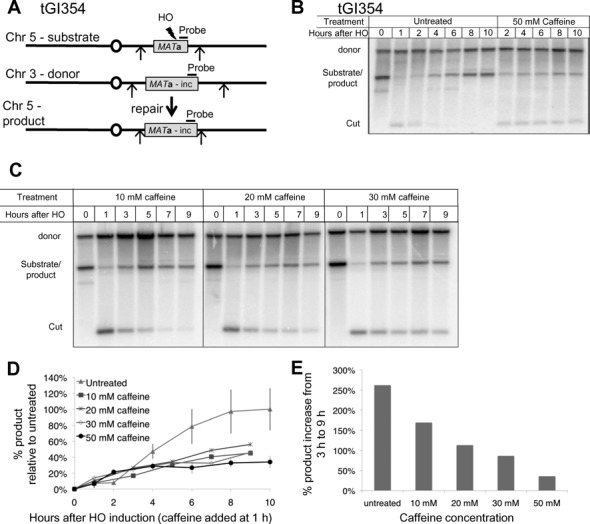
Caffeine treatment impairs GC. (A) Diagram of ectopic GC in tGI354. The MATa-inc donor on Chr 3 cannot be cut by HO. Arrows indicate EcoRI restriction sites. (B) Repair in tGI354. Culture split 1 h after HO induction, half treated with 50 mM caffeine. In addition to a marked reduction in product, the HO-cut fragment is more stable because of a defect in resection. (C) Southern blots to assay repair by GC after 10–30 mM caffeine treatment. Caffeine was added 1 h after HO induction. (D) Quantification of repair in tGI354 treated with caffeine at different concentrations 1 h after HO induction. Product signal was normalized to the loading control (donor) and the untreated maximal repair signal (10 h). Untreated n = 3, 10–30 mM caffeine n = 1, 50 mM caffeine n = 3. (E) Percent increase in GC product formation from 3 to 9 h with different caffeine concentrations. Product at 9 h after HO induction (8 h after caffeine treatment) was divided by the product 3 h after HO induction (2 h after caffeine treatment).
