Figure 1.
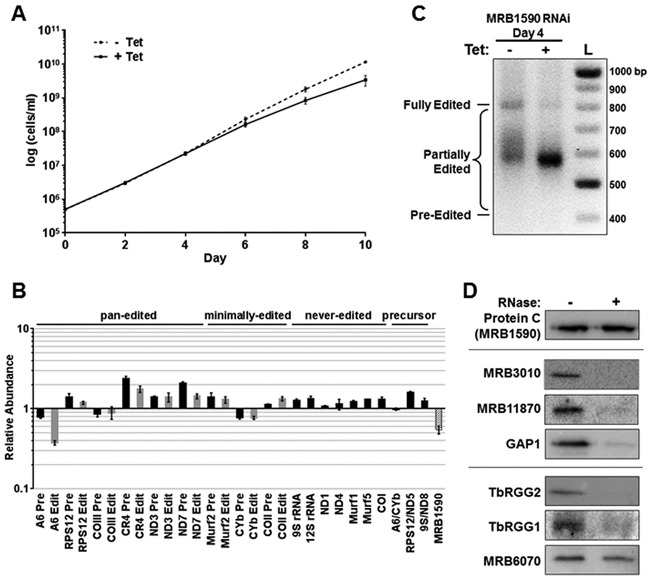
MRB1590 function and interactions in vivo. (A) Growth was monitored for 10 days in triplicate cultures of procyclic form MRB1590 RNAi cells in which MRB1590 downregulation was either uninduced (dotted line) or induced by addition of 2.5 μg/ml tetracycline (solid line). The data are presented as the average ± standard deviation of triplicate determinations. (B) RNA was isolated from procyclic form MRB1590 RNAi cells on day 4 post-induction with tetracycline. RNAs were quantified by qRT-PCR using primer sets specific for selected never-edited, pan-edited, minimally-edited, dicistronic precursor, and MRB1590 RNAs. Relative RNA abundance indicates RNA levels in tetracycline-induced cells compared to those in uninduced cells. RNA levels were standardized to tubulin (n = 5–13), and numbers represent the mean and standard error. (C) Agarose gel analysis of A6 RT-PCR reactions using RNAs isolated from MRB1590 RNAi cells that were grown in the absence or presence of tetracycline for 4 days. Reverse transcription was carried out with an oligo(dT) primer and PCR was done with primers specific to the 5′ and 3′ ends of the A6 mRNA to amplify the entire population of mRNAs including pre-edited, partially edited, and fully edited. (D) MRB1590-PTP and associated proteins were isolated by IgG Sepharose chromatography and TEV protease cleavage from untreated or RNase-treated extracts of cells expressing a C-terminal PTP-tagged MRB1590. TEV elutions were analyzed by western blot for MRB1 complex components using the antibodies indicated.
